In this article, you'll gain a comprehensive understanding of rotating proxies, including their functionality, benefits, applications, and limitations. Learn how these proxies dynamically change IP addresses to increase online anonymity and security, making them ideal for tasks that require high levels of privacy, such as web scraping and accessing websites from multiple IP addresses.
Explore the different types of rotating proxies-data center, residential, and mobile-and understand when and why to use them effectively.
We also discuss ProxyCompass' services and provide insight into what to expect when using their rotating proxy packages.
Need fast rotating proxies for your business?
Check out our pricing for rotating proxies.
What are Rotating Proxies?
Rotating proxies, also known as dynamic proxies, automatically assign a new IP address from their pool to each of your web requests, either per request or at regular intervals such as 1, 5, or 30 minutes.
For example, you could send 1,000 different requests to a website, and each request would appear from a unique IP address.
This frequent changing of IP addresses increases anonymity and prevents detection by web services, which may block access if they detect multiple requests coming from the same IP.
How Do Rotating Proxies Work?
Unlike traditional proxies, which are known as static proxies and have an IP address that does not change over time, the operation of rotating proxies is much more complex.
Let's take a closer look at how rotating proxies work using the diagram below.
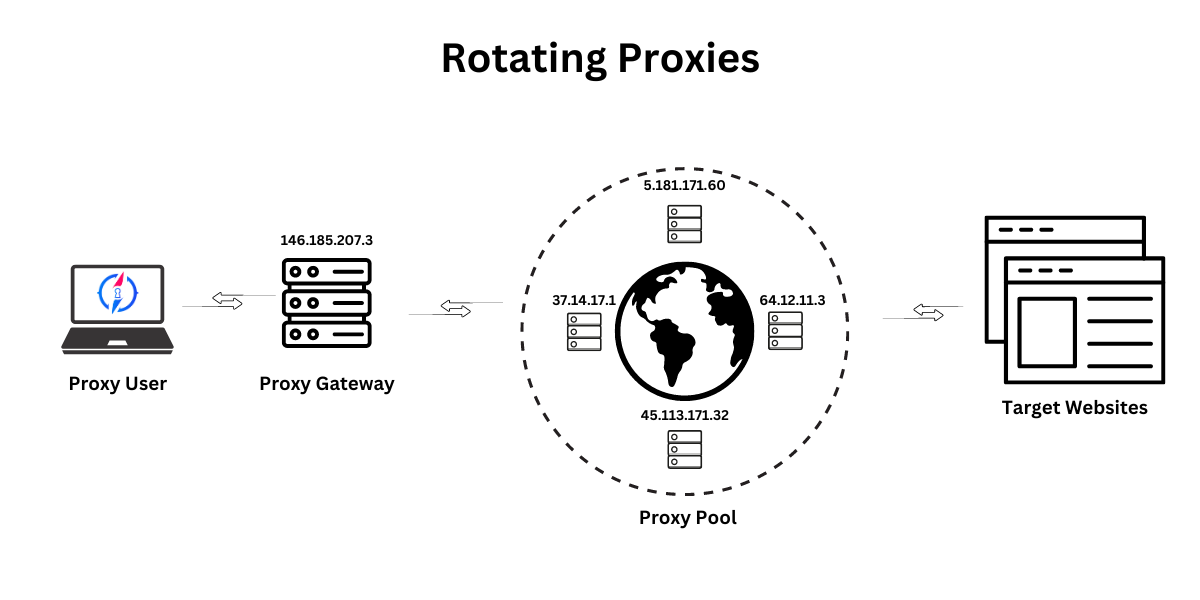
Rotating proxies involve several key components: the proxy user, the proxy gateway, the proxy pool, and the target sites.
Here's how it works in theory:
Proxy User: This is you or any other user who sends a request through the proxy service.
Proxy Gateway: Acts as an intermediary that receives the user's request and then forwards it to one of the end proxies.
Proxy Pool: Contains many end proxy IPs. The gateway selects an IP from this pool each time a request is made, ensuring that each request appears to come from a different IP address.
Target websites: These are the websites that the user wants to access through the proxy.
As a result, the rotating proxy system allows the user to access target sites while constantly changing the originating IP address, which increases anonymity and reduces the likelihood of being blocked or restricted by the target sites.
Here's how it works in practice:
The user of the proxy service does not specify the IP address of the final proxy server in his software settings (browser, bot, curl, etc.), but the IP address of the proxy gateway.
In our diagram, this IP is 146.185.207.3.
The proxy gateway chooses a random proxy from the pool and sends the request through it.
The destination site only sees the IP address of this random end proxy, not the IP address of the gateway or the real IP address of the user of the proxy service.
Thus, the user's real address is hidden behind two barriers.
Characteristics of Rotating Proxies
Avoid IP Blocks: Rotating proxies are critical to extensive data scraping because they frequently change your IP address to avoid bans and detection by websites.
Increased Security: The frequent IP changes offered by rotating proxies add an extra layer of security, making it difficult to trace your online activities.
Superior Anonymity: Rotating proxies assign a new IP for each request, greatly enhancing privacy and anonymity, which is especially useful for private web browsing or accessing content with geographic restrictions.
Different Types of Rotating Proxies
Rotating proxy servers can be divided into several main types based on their origin. For better understanding, we will list the main types below.
Data Center Hosted Rotating Proxies
This is the least expensive and fastest type of rotating proxy services. The entire infrastructure of such a proxy service, including proxy gateways that distribute client requests (also known as balancers) and the end proxies, is located in data centers.
The advantages of these proxy services include unlimited traffic, excellent connection speed, and low service costs.
The downside is that because the IP addresses are owned by the hosting providers, they are more easily identified and potentially blocked by target websites. For complex tasks involving anti-scraping measures, these proxies may not be appropriate.
Learn more about datacenter-hosted proxies.
Residential Rotating Proxies
Residential rotating proxy services are more expensive and slower than data center proxies. Only a small portion of their infrastructure, especially the gateway, is located in data centers. The rest, overwhelmingly 99%, runs on the devices of home users - phones, tablets, and laptops - who offer their devices as hosts for the proxy network.
Residential rotating proxies are highly trusted, able to bypass anti-scraping measures, and offer detailed targeting options down to specific cities within countries.
However, their drawbacks include unstable connections, variable speeds, potential disconnections if the device goes offline, and most importantly, high costs, as users pay for the amount of traffic they use.
Learn more about residential proxies.
Mobile Rotating Proxies
Mobile rotating proxies are a unique type of proxy that reside in mobile farms and are inherently rotating by default. Users of mobile proxy services send requests to a mobile proxy gateway, which then forwards the request to a mobile device with its own SIM card IP address from a mobile operator, which in turn forwards the request to the target website's server.
The advantages of mobile rotating proxies are their high reliability and speed. However, they also have drawbacks, such as high cost, a limited number of IP addresses in the pool, and a limited choice of mobile operators, which can increase the likelihood of detection by sites with strong anti-scraping protection.
Learn more about mobile proxies.
When to Use Rotating Proxies
Rotating proxies are highly effective for activities that require frequent IP changes to maintain anonymity, especially for extensive data scraping from sites that have anti-scraping mechanisms.
Using a single IP for too many requests can lead to throttling, CAPTCHAs, and potential bans, which rotating proxies help avoid by frequently changing your IP.
This increases security and reduces the risk of being detected and blocked by target websites.
When Not to Use Rotating Proxies
It's not recommended to use rotating proxies for tasks that require a constant IP address, such as developing and managing social media profiles. Frequent IP changes can lead to bans.
In addition, rotating proxies are unsuitable for multi-step processes, such as adding items to a shopping cart and completing a purchase, because changing IPs can disrupt the completion of the transaction.
Also, if you need to log in to a destination site, avoid using rotating proxies to prevent account bans and losses.
Rotating Proxies at ProxyCompass: What to Expect
As a customer of our proxy service Proxy Compass, you have the option to choose a rotating proxy package based on the number of requests you plan to make in a month.
Number of requests in package: Our plans are based on the number of requests. The smallest package is 2 million requests. If you're unsure of your needs, start with the smallest package or we can provide a free trial package.
Traffic volume: Traffic is unlimited.
Authentication method: The only authentication method is username and password.
Protocol support: Each proxy supports popular protocols - HTTP/HTTPS and SOCKS5.
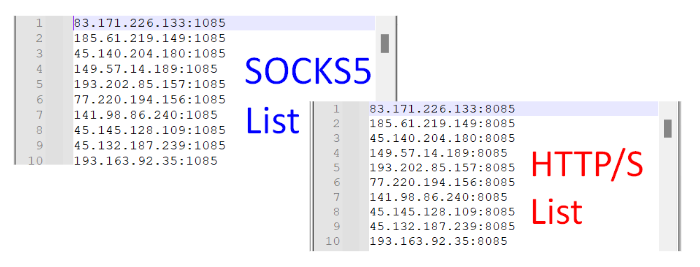
Number of Gateways: Each user is provided with 16 HTTP/S and 16 SOCKS5 gateways or ports (see screenshot below). Users can use any or all of the 32 gateways simultaneously if they need a large number of proxies at once.
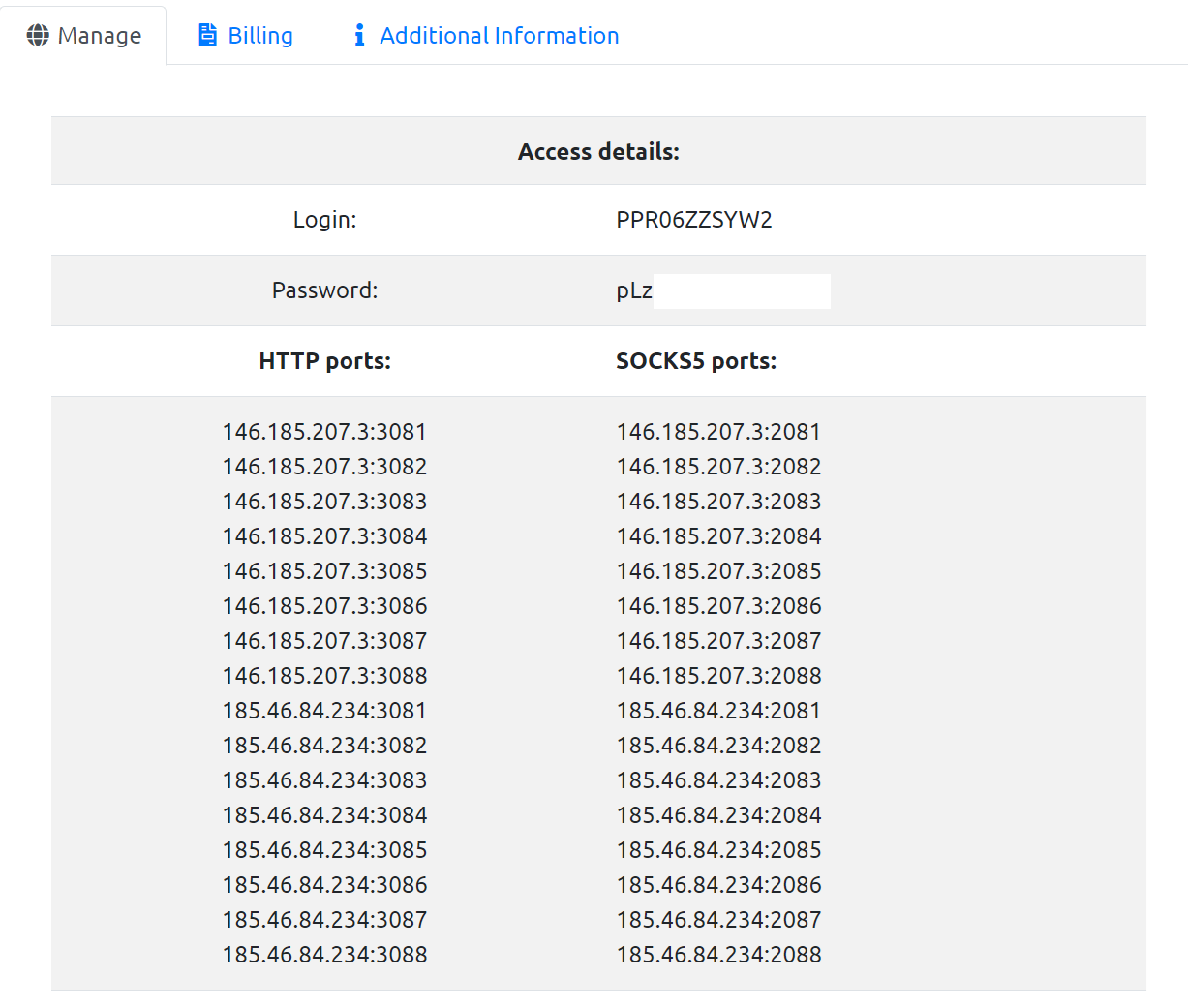
List of
available gateways (ports).
Each of these gateways has its own pool consisting of many thousands of end proxy IP addresses.
Proxy geolocation: Rotating proxies from ProxyCompass are not location based. Users will receive a mix of IP addresses from different countries.
How to Use Rotating Proxies
Rotating proxies are most effective when used with headless browsers such as Puppeteer, Selenium, or Playwright. These browsers do not make side connections and will block all extraneous connections when a page loads, such as ads, counters, and various other scripts that are present in large numbers on every web page. By blocking these, you save the use of rotating proxies.
However, for simplicity and clarity, we will demonstrate the connection of rotating proxies in a regular browser. We will use Firefox with the FoxyProxy extension.
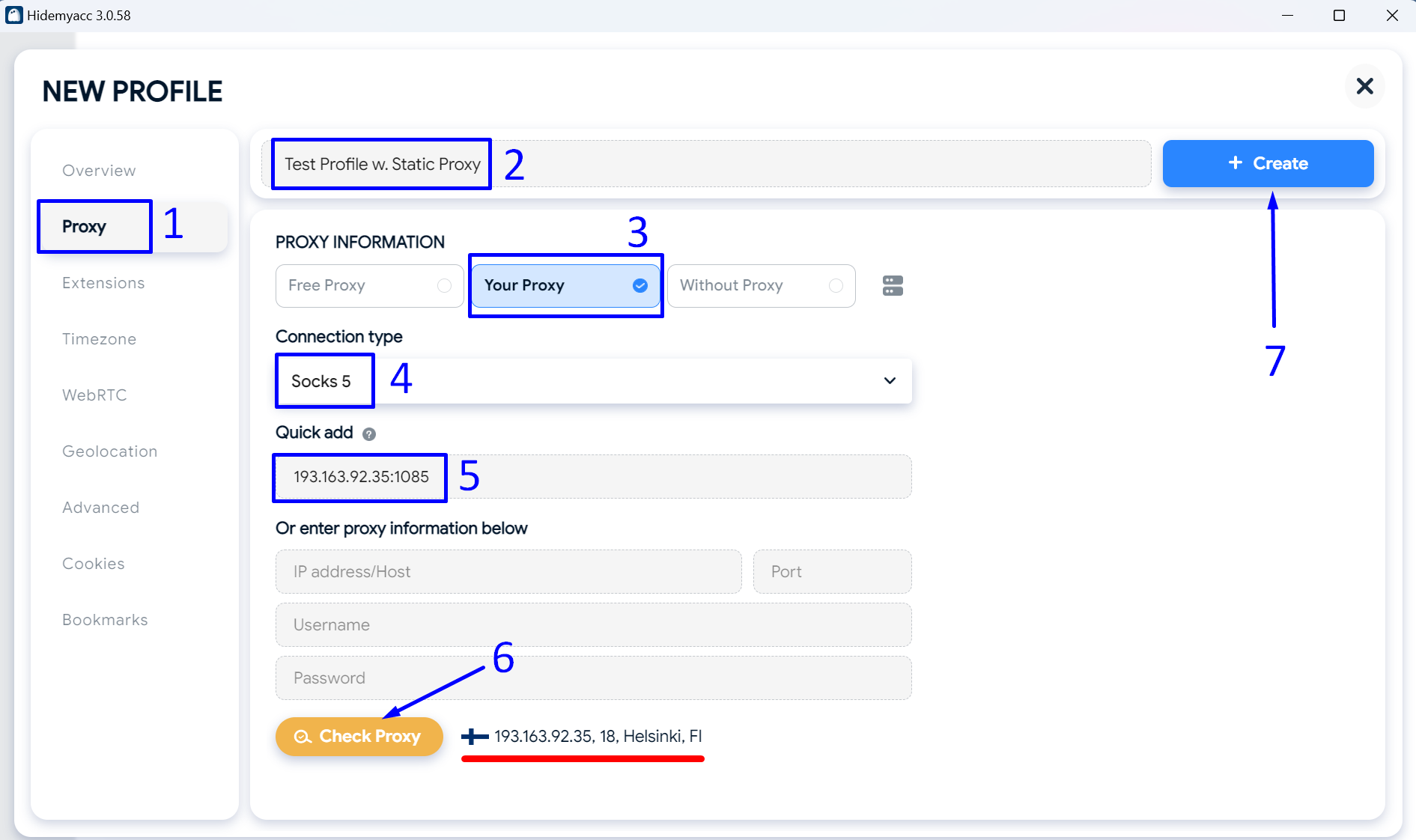
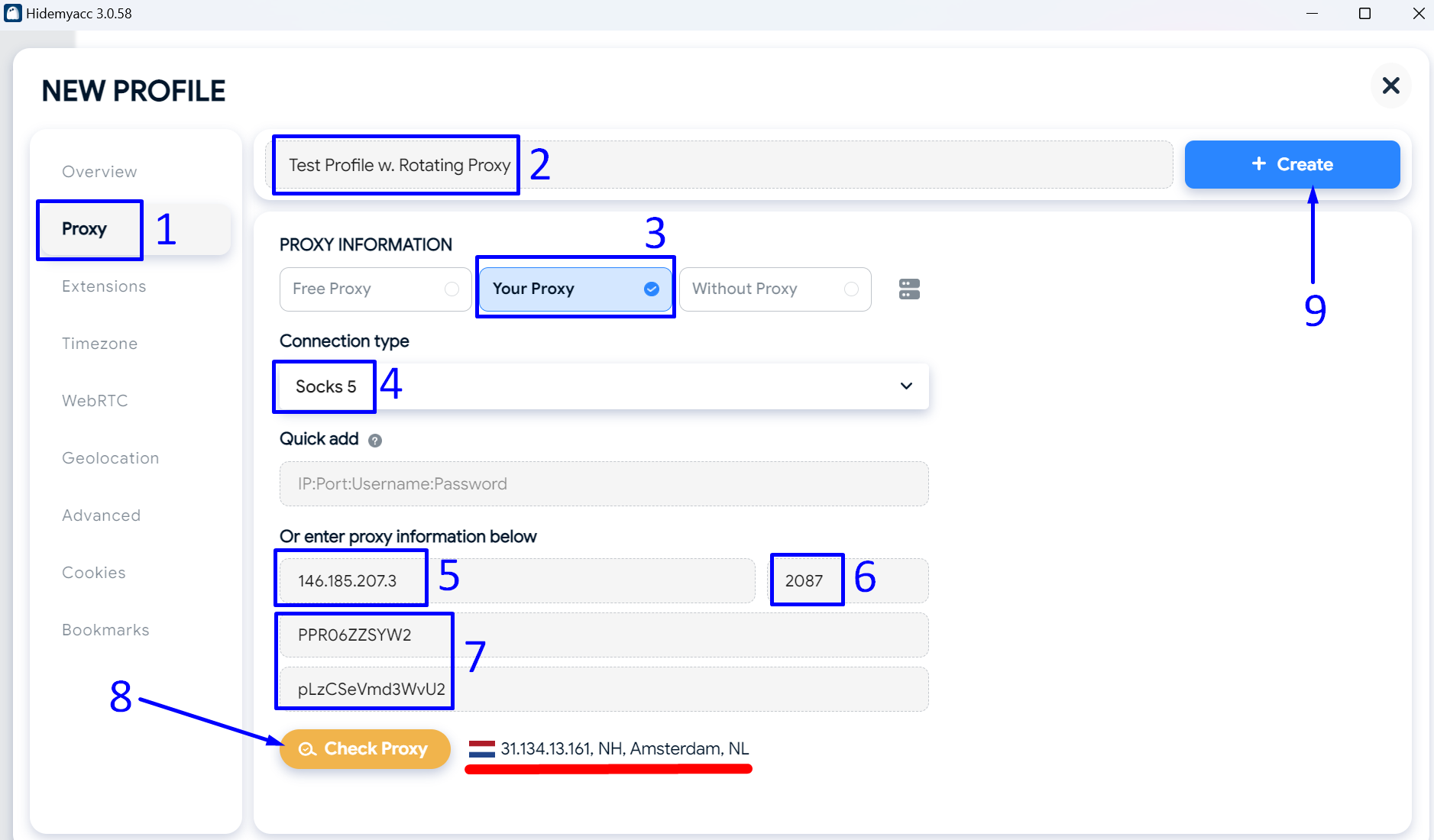
Setting Up Rotating Proxies in Firefox with FoxyProxy
Open Firefox and download FoxyProxy Standard from the official add-on page.
Go to the FoxyProxy settings and create a new proxy connection. In another browser tab, keep open the page with the details of the rotating proxy package you purchased from ProxyCompass.
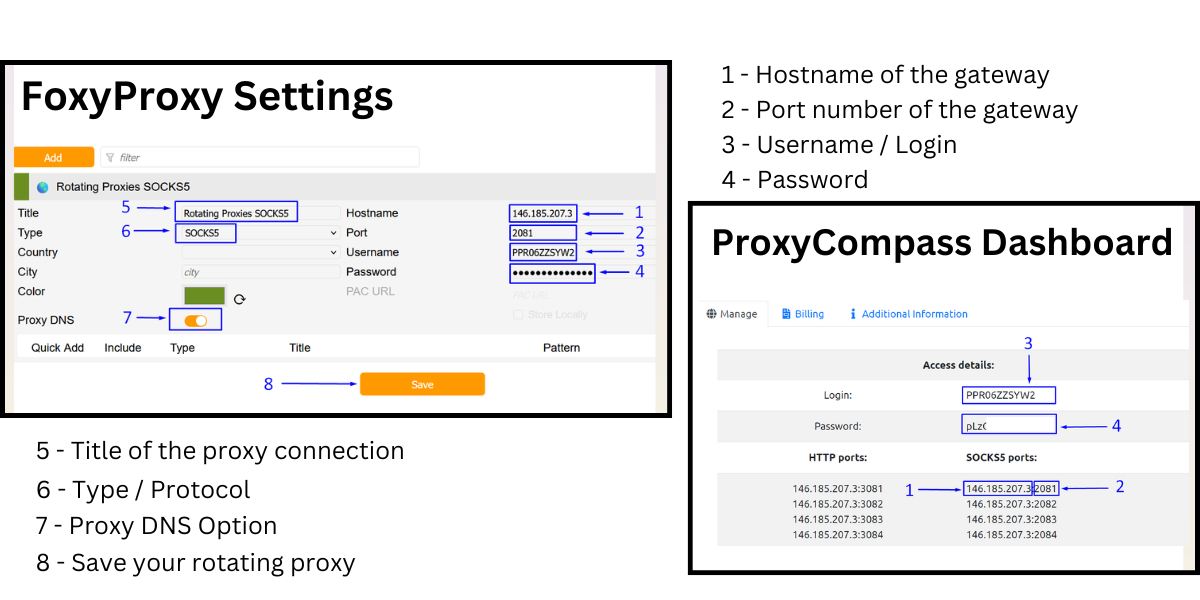
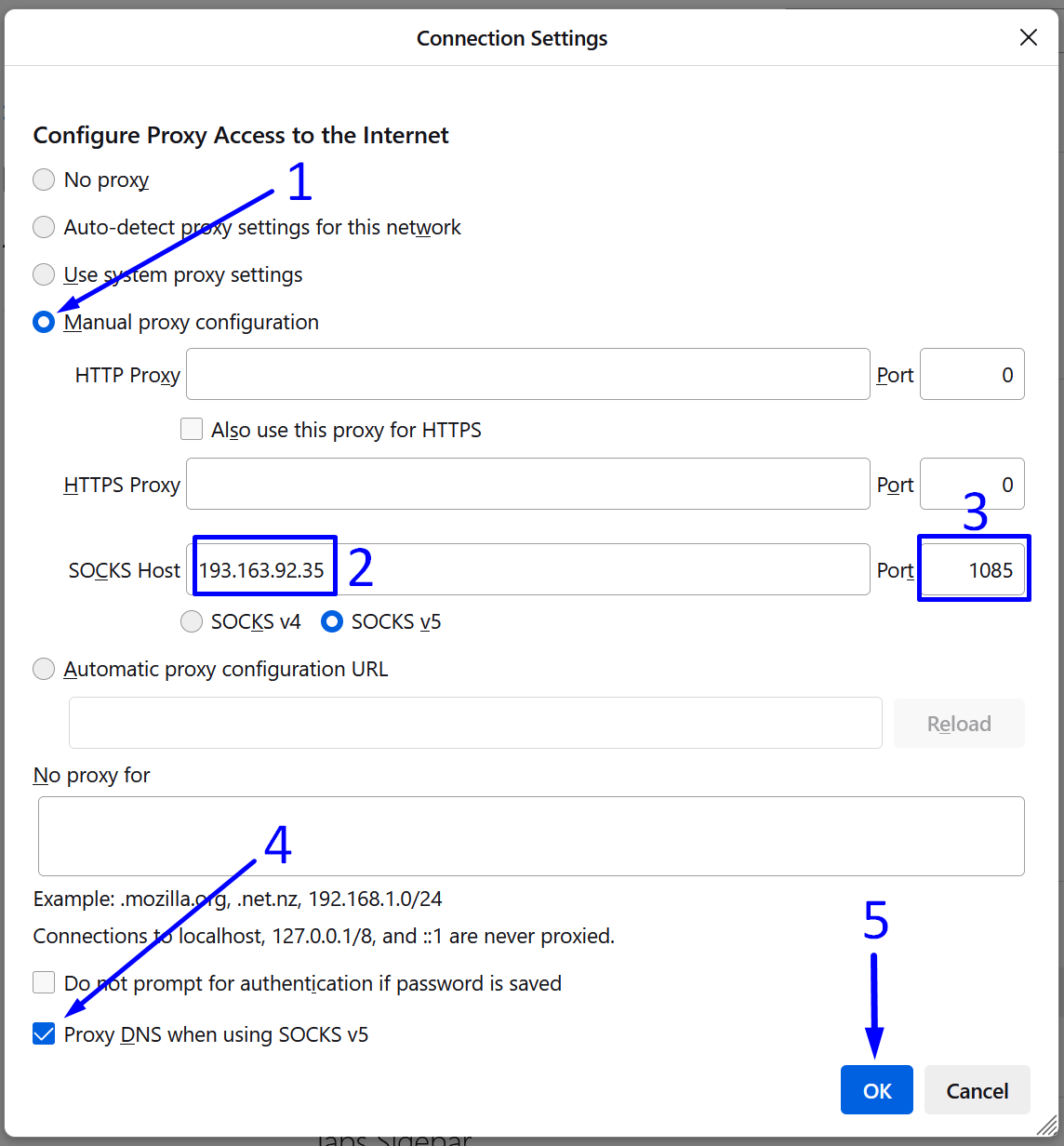
Creating a New Rotating SOCKS5 Connection Step-by-Step:
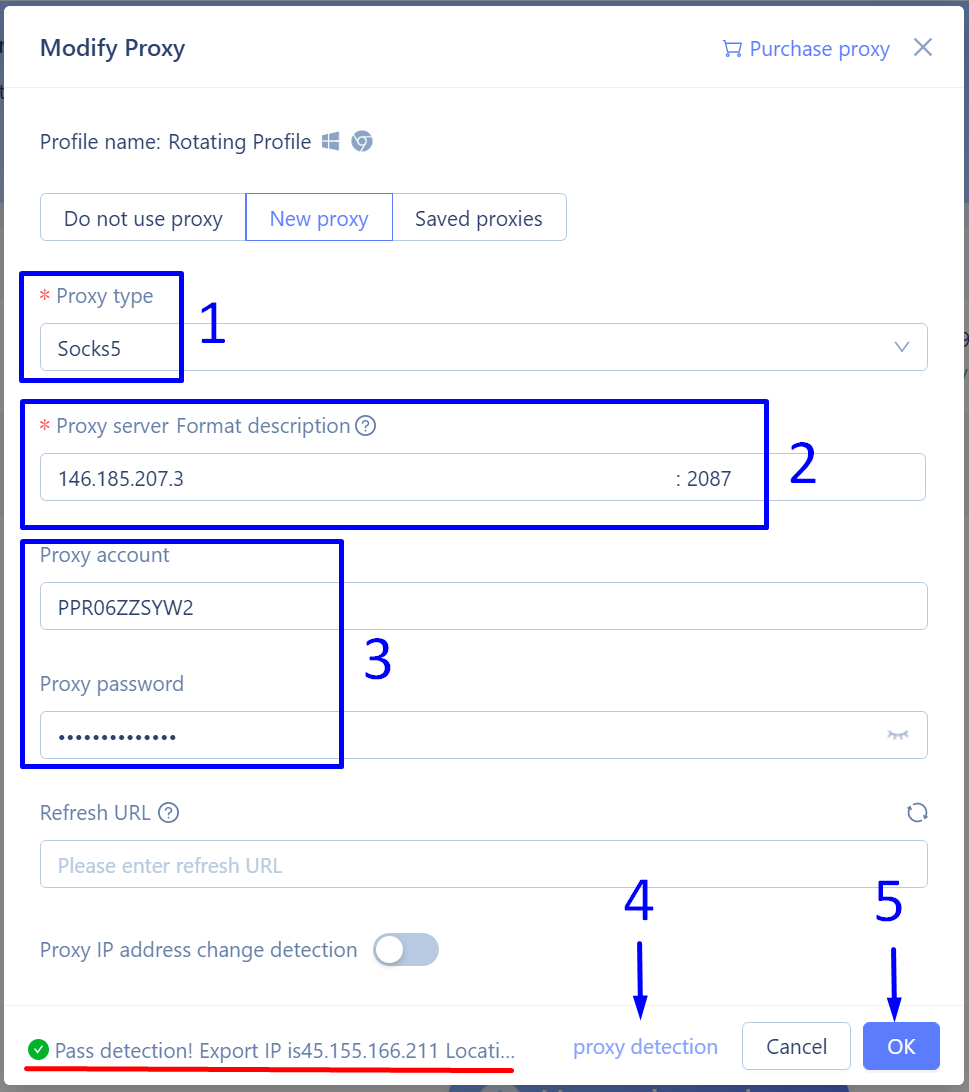
- Copy one of the SOCKS gateway IP addresses from the ProxyCompass page. You will see many available gateways and can choose any of them.
We chose the first one from the list:
146.185.207.3.
Paste the copied IP into the "
Hostname" field in FoxyProxy.
- Copy one of the available ports: 2081, 2082, 2083, etc. Any of them will work. We chose
2081.
Paste it into the "
Port" field in FoxyProxy.
- Copy your unique username and paste it into the "
Username" field in FoxyProxy.
- Copy your unique password and paste it into the "
Password" field in FoxyProxy.
- Come up with a memorable name for your connection in FoxyProxy and enter it into the "
Title" field. We named it
Rotating Proxies SOCKS5.
- In the "
Type" field, select the protocol for the proxy connection. Choose
SOCKS5 as it is the most anonymous and versatile protocol.
- Toggle the "
Proxy DNS" slider to the active position. This feature provides an additional level of anonymity since all DNS requests will be handled through our proxies rather than bypassing them. The SOCKS5 protocol allows for this, unlike the more basic SOCKS4.
- Save the settings by clicking the "
Save" button.
Everything is set. Now, when you activate this profile in FoxyProxy, all your actions in the browser will go through the proxy, changing the IP each time you perform an action in the browser.
How to Test the Functionality of Rotating Proxies
To check if the rotating proxies are working correctly and if you really get a new IP address with every action in the browser, you can visit an IP address checking site. There are many such IP check sites, but not all of them are suitable for our needs.
Why not every IP address lookup page works correctly?
Most of these sites cache the visitor's IP address for a while and do not display the updated address. We need to make sure that we get a new IP address every time. Caching will interfere with this process.
Below is an example of a suitable page where caching does not occur and the updated IP address is correctly recognized:
https://chekfast.zennolab.com
If you follow the link above and refresh the page each time, you will see that your IP address is indeed changing.
To demonstrate the functionality of rotating proxies, we have prepared a video that shows how each action in the browser results in a new IP address. Watch the video below to see rotating proxies in action.
https://youtu.be/5RgQ3evCAF4
As you can see in the video, our proxy IP changes with each new request. The setup and testing are complete.
Thank you for reading the article to the end. We hope you found it helpful.
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/rotating-proxies-explained/










 List of available gateways (ports).
List of available gateways (ports). 

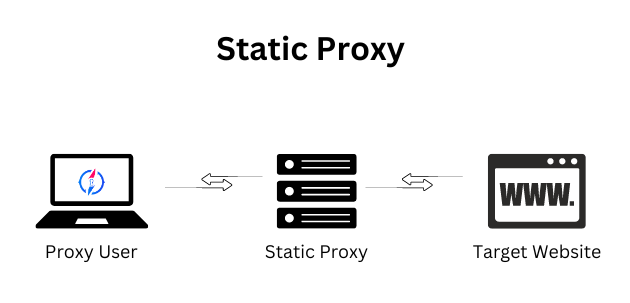
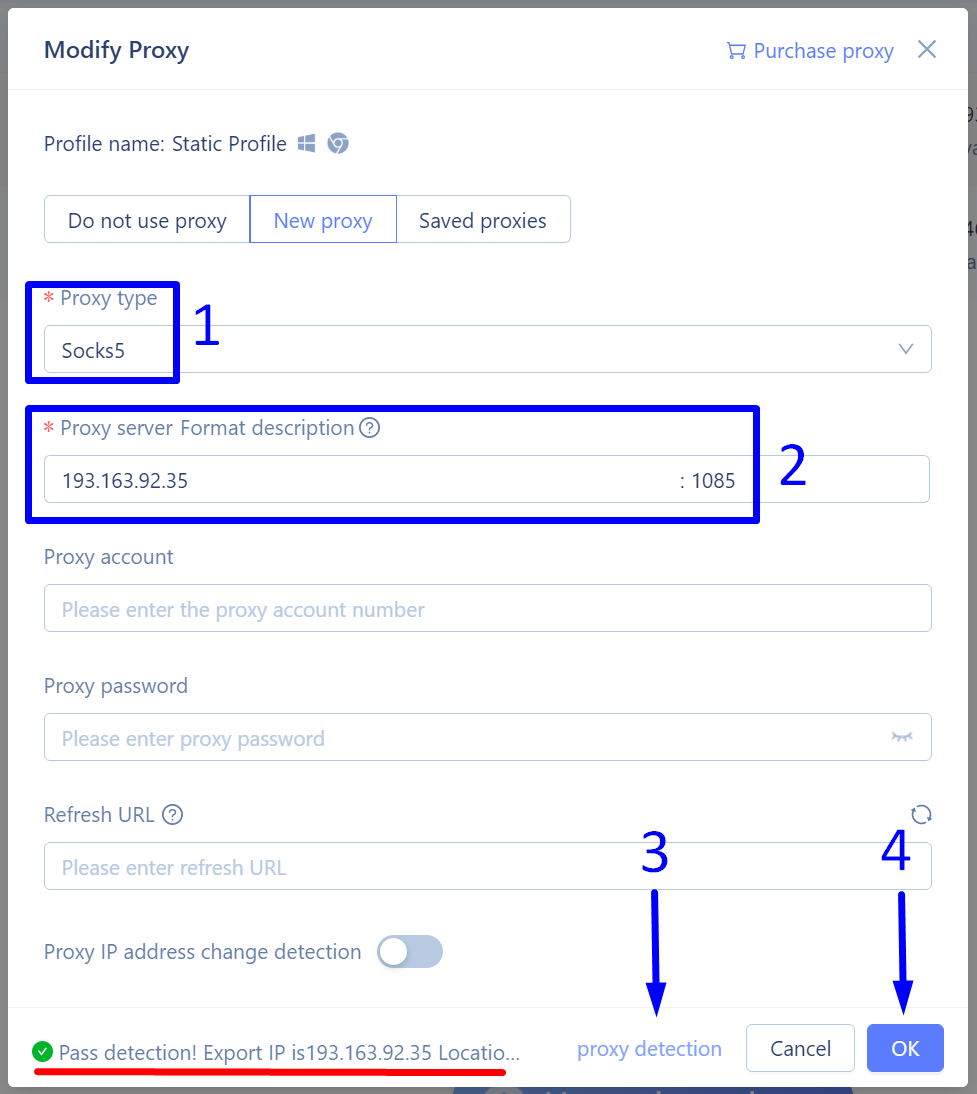
 Static proxies are available for simultaneous use over both SOCKS5 and HTTP/S protocols.
Static proxies are available for simultaneous use over both SOCKS5 and HTTP/S protocols.