Freitag, 31. Mai 2024
A private proxy is an exclusive proxy server that can only be assigned to one owner. It is used to hide one' s own proxy IP and thus create a certain degree of anonymity.
If a proxy of this kind is booked with a provider, it is exclusively available to this customer for the booking period and can only be assigned to other customers after the end of the contract. This means that every private proxy is available for a period of at least one month with the customer and only the customer can use it.
You can explore various options and purchase a private proxy that suits your specific needs by visiting the Private Proxies Pricing Page. To ensure complete control and privacy, opting for a private proxy is a solid choice.
Difference between private and public proxies
Unlike a public proxy server, dedicated or private proxies are protected and can only be used with a user name and password.
Furthermore, with a dedicated proxy server, the IP address always remains the same and cannot be changed. One advantage of dedicated proxies is their very high connection speed and permanent availability. Due to this unlimited availability of a private proxy server, the connection is always stable.
Private proxies are usually less constrained by the proxy provider than shared proxies. This means that the customer who uses them has the possibility to open more simultaneous connections to certain websites.
Since a private proxy returns to the proxy pool after being used by a customer with an expired contract, and a new customer is assigned to it, it can also be negatively charged. For example, if the previous customer visited certain sensitive sites, the proxy address may have been banned.
So before purchase (if there is a free trial) or immediately after payment during the warranty period (usually 1-2 days) you should make sure that the IP data is not blocked on the target site. In such cases, the provider usually offers a replacement or refund.
Basically, all proxy providers must pledge not to disclose the data to third parties, but the data and activities are registered with the service provider and can thus be attributed to a customer. So if you are mainly looking for good speed and have nothing to hide, you should choose a private proxy, because their performance is convincing.
Even those who want to access content that is not displayed by their own conventional IP address can circumvent the problem by using a private proxy. Streaming services, for example, do not offer all content in every country and by using a private proxy, the customer can change their location and thus have access to the content.
Private Ports
The equivalent of private proxies for mobile proxy services are so-called private ports. However, these private ports may not only be used in mobile device settings, but generally in any device such as laptop, phone, VPS, etc.
This means that if the customer is looking for a way to access the Internet via a mobile IP address or to use his bot so that the target site perceives this visitor as if he was using a smartphone, this person must use the services of a mobile proxy provider.
Mobile proxy services are divided into private and shared IPs. If the customer only needs (private) proxies dedicated to them, a private port is assigned to them. This is a specific IP address (gateway IP) and a non-standard port. The IP addresses that the customer receives at the exit (exit IPs) are only available for this customer. How this works is explained in the article "What are mobile proxies?”
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/what-are-private-proxies/
Donnerstag, 30. Mai 2024
What are Virgin Proxies?
Virgin proxies are IP addresses that have never been used before as proxies. A data center virgin proxy runs on the IPv4 protocol. However, IPv4 addresses have not been able to be registered for a long time - all available subnets were already registered to different companies as early as 2012.
The situation with IPv4 is similar to the situation with short .com and .org domains: You can buy such IPs, but only privately from other companies or even through an auction. Also, this is only possible for a company registered in a particular way, the purchase is not possible for average consumers.
IPv6 proxies, on the other hand, are almost always "virgin", due to their almost inexhaustible number, cheap price, and the ease of registering new IPs of this kind.
Many proxy vendors offer this kind of proxies partly for specific services. For example, Instagram proxies, which have never been used in any of the social networks, but probably for other online activities.
Where do Virgin proxies come from?
These proxies come from an organization called LIR (Local Internet Registry). The LIR owns a block of IP addresses that are provided by the RIR, the Regional Internet Registry.
LIRs consist of Internet Service Providers, businesses, and academic institutions. Proxy providers usually buy these proxies from LIRs and other companies in small blocks. Each block is analyzed to ensure that it is truly clean.
There are five regional Internet registries around the world. The RIRs manage all Virgin IP addresses for their respective regions. The Réseaux IP Européens, or abbreviated RIPE, is responsible for Europe.
What can be expected when buying virgin proxies?
Virgin proxies operate with any online resources specified by the provider that allows data center proxies to operate with them (unless the provider has explicitly restricted their use. See Chapter #6: Restrictions and Prohibitions)
These proxies play an important role in social media. The only way to avoid being banned is to use clean proxies.
Since a clean proxy is not associated with any account, has no history, you don't need to worry about a social media ban. You are only responsible for your own actions, not the actions of others. This means that as long as you comply with the terms of use, you won't run into problems. It's similar to logging in with your own IP address, only your identity is hidden.
Also, virgin proxies are not on the blacklist ("ban") of Google services, including Google Search and Google Mail, and are not on the blacklists of Spamhaus, etc
Nuances and possible pitfalls
- It is almost impossible for ordinary users to buy virgin proxies, i.e. unused IPs, these days. This is due to the following reasons:
- It is a stroke of luck if a provider manages to buy subnets that have never been used for hosting or proxy services
- Most likely, the proxy provider must have paid a considerable price for these "pure" IPs, and accordingly, they will not sell them cheaply, i.e. certainly not for $2-5 US dollars for an IP address (this is the average price of a private proxy)
- The proxy provider will not let you "test" these IPs before purchasing them. Because the probability that they are still "clean" after the test is somewhat low
- The proxy provider will most likely not refund the buyers' money after the purchase if they are not satisfied
- It is in the interest of the proxy provider to sell these IPs directly in one large package, preferably the entire /24 subnet (256 addresses), i.e. x.x.x.0 - x.x.x.255.
However, this approach is contrary to the interests of the buyer, because he usually does not need so many IPs. The buyer usually only needs 20-100 IPs, preferably from different subnets, and all of them should be "virgin" ̶ which is simply impossible nowadays.
If the buyer nevertheless decides to buy the whole subnet, he will get consecutive IPs x.x.x.x.0, x.x.x.1, x.x.x.2 ... x.x.x.255, which is a very strong footprint and will most likely lead to an immediate ban of this subnet.
"Real" virgin proxies are extremely rare today and thus expensive. Also, they are almost always sold at unfavorable conditions for the customer. So if you are interested in buying them, you should weigh up the pros and cons twice and clarify all details with the vendor before buying.
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/what-are-virgin-proxies/
Mittwoch, 29. Mai 2024
At the same time, and depending on the type, proxies conceal some information about your online identity. Examples of data concealed include your IP address and location.
Indeed, there are several types of proxies. And they can be broadly categorized into four groups based on the following:
- Protocol, i.e., SOCKS proxies and HTTP and HTTPS proxies
- Number of active users, i.e., shared proxies, private proxies, and virgin proxies
- The direction of traffic routing, i.e., forward proxies and reverse proxies
- The type of IP address assigned, i.e., residential proxies, data center proxies, and mobile proxies
However, this article will mainly focus on proxies identifiable by the protocol used to communicate online. This category includes SOCKS proxies and HTTP and HTTPS proxies.
What Is a SOCKS Proxy Server?
A SOCKS proxy is an intermediary that utilizes the SOCKS protocol to facilitate network connectivity between hosts or between a web client and a web server through a firewall. This proxy runs software known as a SOCKS daemon. The software is specifically installed at a firewall host (machine on which a firewall has been installed), creating a secure route through this firewall.
Therefore, this means the SOCKS protocol does not bypass firewalls but rather allows communication to be routed through the firewall via a proxy server. Accordingly, the firewall blocks all unauthorized traffic as well as traffic that does not conform to certain parameters, such as the username or that which has not been sent using the SOCKS protocol.
However, suppose the communication is sent via this protocol and, by extension, via the SOCKS proxy. In that case, the users will access the internet or be able to communicate with other computers in an external network. Generally, the SOCKS proxy server supports application-level connections, i.e., those sent via application layer protocols, pass. (Application layer protocols include HTTP, HTTPS, SMTP, TELNET, FTP, POP, MIME, and more.)
How a SOCKS Proxy Server Works
As a result of this arrangement, users’ computers, collectively known as hosts, utilize the SOCKS proxy server as a secure transient point that enables secure communication with other hosts or web servers. And given that a network firewall or firewall host still protects the connection through this intermediary, it prevents unwanted intruders from accessing the communication between the hosts. Thus, only parties with accounts on the host (proxy account) can access network packets sent using the SOCKS protocol through the firewall.
The SOCKS proxy server not only enables the communication between users’ computers but also between web clients and web servers. And as is the case with all other proxy servers, it intermediates network traffic, blocking direct access. Thus, when a client sends HTTP, HTTPS, or FTP requests, the SOCKS server receives them and subsequently serves them to the web server on the client’s behalf. At the same time, it receives responses from the server and forwards them to the client. However, before discussing SOCKS proxy servers in greater detail, let’s first understand the SOCKS protocol, its history, and how it works.
History of SOCKS Protocol
The name SOCKS proxy server is derived from a network protocol known as Socket Secure, which is contracted to SOCKS. Based on the above description, the SOCKS protocol provides a framework for network connectivity through a network firewall. The protocol has undergone various improvements since it was first introduced in the early 1990s. And this section will describe the evolution over the years.
SOCKS Version 1
The original SOCKS protocol was proposed in a paper presented at the third USENIX UNIX Security Symposium in 1992. However, at the time of presenting the paper, SOCKS had been running at MIPS Computer Systems for three years. This means SOCKS was originally created on or about 1989.
Authored by David Koblas and Michelle Koblas, the paper discussed how the SOCKS protocol could be used to provide convenient and secure network connectivity through a firewall host. Its creators designed it as a solution to a problem that existed then: the methods of creating a secure environment through that computers could connect to the internet were cumbersome, inconvenient, or could be easily compromised.
The paper presented a SOCKS package, which included the SOCKS library, protocol, and a daemon (SOCKS proxy software). The library included calls that established connections to the SOCKS daemon installed on the firewall. In this way, the library enabled the transmission of information and network connections in such a way that the daemon appeared to be the originator of the requests. Thus, to an external host, the daemon (SOCKS proxy) would appear to be the originator of the requests. The SOCKS library routines or calls included:
- Connect: It requests that the SOCKS proxy (daemon) establishes an outbound connection to a given IP address, port number, and username
- Bind: It requests an inbound connection expected from a given external IP address. It also contains username requirements, but this username belongs to the requestor (sender) and is used for logging the information. Generally, the Bind call binds a new socket connection to a free port on the firewall.
- Listen: It awaits (listens), ready to accept calls from the external host
- GetSOCKName: It gets the IP address and port number of the socket on the firewall
- Accept: It accepts a connection from an external host
SOCKS Version 4 (SOCKS4)
Ying-Da Lee extended the SOCKS protocol, creating SOCKS version 4 (SOCKS4) before later introducing SOCKS version 4a (SOCKS4a). Accordingly, SOCKS4a expanded the protocol’s capabilities by supporting the resolution of the destination host’s (server’s) domain name to find its IP address.
SOCKS Version 5 (SOCKS 5)
In 1996, a group of contributors wrote a memo describing SOCKS version 5. The write-up extended the capabilities of the SOCKS protocol by expanding the capabilities of the underlying framework to enable it to support more sophisticated application layer protocols. Additionally, SOCKS5 introduced support for client-server applications in both the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Further, it extended the addressing system to include IPv6 addresses and domain-name addressing.
Finally, SOCKS5 introduced strong authentication. The new version specifies a generalized framework for using arbitrary authentication protocols. For example, when initiating a SOCKS connection, the following authentications can be used:
- Username/Password sub-negotiation authentication services (However, the username/password sub-negotiation is unsecured and is, therefore, not recommended in cases where hackers or third parties can undertake ‘sniffing.)
- Secure Username and password authentication that uses known host keys and relays the keys through encrypted communication
- GSS-API authentication method
It is noteworthy that the revisions resulted in several types of SOCKS proxies, namely:
- SOCKS4 proxies
- SOCKS5 proxies
SOCKS4 vs. SOCKS5: Similarities and Differences
Similarities Between SOCKS4 and SOCKS5
SOCKS4 and SOCKS5 protocols and, by extension, proxies are similar in the following ways:
- The SOCKS service in SOCKS4 and SOCKS5 is located on port 1080
- They utilize the same operations, i.e., connect, bind, listen, accept, and getSOCKname.
Differences Between SOCKS4 and SOCKS5
SOCKS4 and SOCKS5 protocols and proxies differ in the various ways described in the table below:
SOCKS4
SOCKS5
Supported Domains
It only supports TCP
It supports both TCP and UDP
Security
It provides unsecured firewall traversal because it does not authenticate the network packets
It supports strong authentication schemes, such as username and password requirements, thereby promoting secured firewall traversal
Supported Protocols
It supports FTP, SMTP, TELNET, HTTP, and GOPHER (i.e., application-layer protocols)
It supports FTP, SMTP, TELNET, HTTP, and GOPHER, as well as NTP, DHCP, BOOTP, NNP, TFTP, RTSP, RIP, and DNS (i.e., application and transport-layer protocols)
IP Address
It supports IPv4 addresses only
It supports IPv4 and IPv6 addresses
Domain Name
It is incapable of resolving all domain names and can, therefore, not find their IP addresses
It can resolve all servers’ domain names to find their IP addresses
Addressing
It does not support domain-name addressing
It supports domain-name addressing
How Secure is a SOCKS Proxy Connection?
A SOCKS connection, unlike an HTTPS connection, is not encrypted. But an encrypted HTTPS connection can be established over any SOCKS connection (within the connection), which is completely inaccessible from the outside:
This may look complicated, but in reality, it is very simple, and such a connection is automatically created when the user first establishes a SOCKS connection (e.g. with Proxifier or the browser add-on Foxyproxy) and then goes to a web page that uses an SSL certificate (“lock” to the left of the address bar).
Browser SOCKS (HTTPS ) SOCKS target website
This means that this connection is completely secure, and no one, not even the proxy provider, can find out exactly what the user is doing on the website, what he is printing, what pictures or videos he is viewing or uploading.
Advantages and Disadvantages of SOCKS Proxy Servers
Advantages of SOCKS Proxies
The advantages of SOCKS proxies are:
- Lesser errors: SOCKS proxies, unlike HTTP proxies, do not interpret or rewrite the data packets such as headers. Thus, they are not prone to mislabeling or other errors.
- Support for multiple protocols in the application and transport layers: SOCKS4 proxies support FTP, SMTP, TELNET, HTTP, and GOPHER protocols. In contrast, SOCKS5 proxies support FTP, SMTP, TELNET, HTTP, and GOPHER protocols, as well as NTP, DHCP, BOOTP, NNP, TFTP, RTSP, RIP, and DNS. In contrast, HTTP proxies only support HTTP and HTTPS protocols.
- Better security: SOCKS5 proxies, in particular, undertake authentication at various stages. This promotes security. Generally, however, given that all SOCKS proxies do not interpret or rewrite data, they cannot uncover data packets that contain your personal information.
- Enhanced privacy: SOCKS5 proxies can change your IP address, thus concealing information such as your real location, especially considering that IP addresses store such data.
Disadvantages of SOCKS Proxies
The disadvantages of SOCKS proxies include the following:
- Connection delay/slow speed: SOCKS5 proxies, in particular, have to undertake a number of authentications at different stages of operations, which translates to slower speeds.
- Limited back-connect: The SOCKS5’s bind command does not sufficiently cover protocols that require the server to connect to the client (back-connect) multiple times; instead, it is primarily suitable for protocols such as FTP that require only a single back-connect
- Limited capabilities of supported UDP: SOCKS5’s initial UDP support had limited capabilities. For instance, the protocol envisioned that UDP applications should send data and receive a response. However, many UDP applications can receive UDP data without requiring IP address information, sending data, or using a certain port. Thus, SOCKS5 proxies have limited UDP capabilities.
- Backward incompatibility: SOCKS5 proxies are not backward compatible with the earlier versions of the SOCKS protocol, such as SOCKS4a
How to Use SOCKS Proxies
SOCKS proxies are used in the following ways:
- They allow users to bypass geo-blocking. This way, SOCKS proxies, particularly SOCKS5 proxies, enable them to access content from other locations. (Geo-blocking or geo-restriction is the practice whereby websites only show content to visitors from a specific location.)
- SOCKS proxy servers help bypass internet filtering by schools, workplaces, and governments, just to mention a few
- Anonymous use of messengers, such as Telegram
- Video streaming and live calls
- Torrenting or peer-to-peer sharing and downloading
- Bulk and secure emailing due to SMTP support
- General web browsing because SOCKS5 supports a number of application-level protocols
- Blocking unauthorized access to business networks: SOCKS proxies act as a transient intermediary that enables secure internet access through the business firewall while preventing unwanted intruders from accessing the server or computers within the local network.
SOCKS Proxies vs. HTTP Proxies
As detailed earlier, SOCKS proxies and HTTP proxies are protocol-based proxy servers. For a detailed discussion of what HTTP and HTTPS proxies can achieve, refer to our article on HTTP and HTTPS proxies.
How SOCKS Proxies and HTTP Proxies Compare
This section details the similarities and differences between SOCKS and HTTP proxies.
Similarities between SOCKS Proxies and HTTP Proxies
SOCKS and HTTP proxies are similar in the following ways:
- They are both based on internet protocols
Differences between SOCKS Proxies and HTTP Proxies
SOCKS and HTTP proxies differ in the following ways:
SOCKS Proxies
HTTP Proxies
Protocols
They support a large number of TCP protocols as well as UDP protocols
They only support HTTP and HTTPS protocols
Security
They do not encrypt data
HTTPS proxies encrypt data
Firewall Access
SOCKS proxies provide internet access through a network firewall
They do not provide a connection through firewalls
Data Interpretation
They do not interpret, analyze or rewrite data
They interpret data and, in some cases, rewrite the header packets
Interoperability
SOCKS proxies can use HTTP and HTTPS protocol
HTTP and HTTPS proxies cannot use the SOCKS protocol
OSI Classification
SOCKS proxies are found at a lower level (layer 5) of the OSI classification, i.e., the session layer
HTTP proxies are found on a higher level (layer 4) of the OSI classification, i.e., the transport layer
Configuration
SOCKS proxies can only be integrated into a web client or machine that is not a web server
HTTP proxies can be configured into either the web client or server
Port
SOCKS services are available through the SOCKS proxy ports 1080 and 1085
HTTP proxies utilize ports 80, 8080, 8085, 3128, and 3129, while HTTPS proxies use port 443
SOCKS Proxy vs. VPNs
Granted, SOCKS proxies can create a secure tunnel through a firewall. But did you also know you can create a secure tunnel using a virtual private network or VPN? A VPN creates a secure route of communication between two networks: a local network and external networks. It achieves this by routing all internet traffic through a tunnel, but not before encrypting the data at the point of entry (your computer, for example). The tunnel terminates at an exit node (the VPN’s exit server) that assigns the outgoing requests from a user’s local network or computer a new IP address, effectively concealing the real IP address.
When using a VPN, all requests appear to originate from the exit note. At the same time, all responses from a web server appear to terminate at this VPN server. Thanks to this arrangement, you can use a VPN to access otherwise geo-blocked content of any location in which the VPN provider has a server.
For instance, if you are located in Germany and would like to access web content that is only viewable to residents in the United States, you can simply use a US-based VPN server.
To do this, you must first install VPN software on your computer, which will convert your machine into an entry node. The software is responsible for encrypting the data. Next, you will have to choose the exit node, and once the VPN connects to this exit server, you are free to send your request.
Advantages of VPNs
The pros of virtual private networks include:
- Encryption and security: VPNs encrypt all requests and server responses, thus guaranteeing unmatched security. It is for this reason that you are advised to use a VPN whenever accessing the internet through public Wi-Fi
- Provide access to geo-blocked content: A VPN virtually transports you to that location by routing traffic through an exit node in a different country. As a result, you can access web content that you would otherwise not have been able to in your home country without the VPN.
- Online privacy: VPNs hide your real IP address and subsequently assign a different address. This way, they protect your online privacy by concealing certain data about you, such as your location (state, city, country, and approximate coordinates).
Disadvantages of VPNs
The cons of virtual private networks include:
- Slow connection speeds: Because this solution has to encrypt all outgoing requests and incoming responses, it is usually slower.
- Logging user data: Another common downside that has led to uproar among VPN users is that some VPN providers often log user data. They do this in order to subsequently furnish law enforcement officials with the said data when prompted. In fact, several providers have made headlines by furnishing investigation bodies with user data. Moreover, some countries, such as India, have laws mandating VPN providers to save user data. Against this backdrop, observers have previously advised users to take providers’ ‘No logs’ policy at face value.
- Free VPNs are generally unsafe: Such VPNs often share the same secure tunnel among multiple users, which can increase the chances of ‘sniffing’ or eavesdropping.
- VPNs are banned in certain countries: some countries have made the use of VPNs outright illegal. In other nations, only government-licensed VPNs can be used.
Uses of VPNs
Virtual private networks are used in the following ways:
- VPNs provide security when accessing the internet through public access points
- Accessing geo-blocked content: as stated, VPNs, like SOCKS5 proxies, allow you to access any content from any location
- Facilitate remote work: companies safeguard their data by requiring their remote workers to log into their systems or servers through dedicated VPNs
How do SOCKS Proxies Compare to VPNs
Recalling the above-mentioned features, advantages, and disadvantages of SOCKS proxies, how do SOCKS proxies vs. VPNs compare?
Similarities between SOCKS Proxies and VPNs
SOCKS proxies and VPNs bear certain similarities, including:
- Online privacy: SOCKS5 proxies and VPNs conceal real IP addresses, thus offering online privacy
- Security: both solutions boost security, albeit in different ways. VPNs encrypt the data while SOCKS5 proxies perform authentication.
- Supported protocols: some VPN protocols, such as OpenVPN, support TCP and UDP, while SOCKS5 proxies also support TCP and UDP.
- Bypassing geo-restrictions: SOCKS5 proxies and VPNs can be used to access otherwise geo-blocked content.
Differences between SOCKS Proxies and VPNs
SOCKS proxy servers and VPNs differ in a few ways.
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/what-are-socks-proxies/
Dienstag, 28. Mai 2024
But first, let us discuss the protocols on which HTTP proxies and HTTPS proxies are based.
Understanding HTTP and HTTPS
What is HTTP?
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol or HTTP is a stateless, application-level protocol that facilitates communication between client applications (such as web browsers and web apps) and web servers (or web user interface servers).
It is a layer 7 protocol (or application layer protocol), meaning it is meant to transmit data between the server and client and vice versa. HTTP generally supports the transmission of a variety of data types. These include text, video, and audio data, collectively known as hypermedia.
When a client wants access to this data, which is stored on a server, it sends an HTTP request. Generally, the HTTP request contains the following:
- A request line that specifies the HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, and so on), HTTP version (below), and additional information about the request’s target (hostname and port)
- Headers, which store additional information, e.g., cookies
- Body of the request message
Upon receiving the request and interpreting the message, the server then sends an HTTP response containing the requested data.
How Does HTTP Work?
It is worth pointing out that HTTP does not perform its functions in isolation. In fact, it runs on top of transport layer protocols (layer 4), such as Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Furthermore, it was also built over the IP protocol, which existed at the time.
On their part, these layer 4 protocols establish, manage, and close communication between a server and a client (networked devices). To put it simply, TCP and UDP allow networking applications, which sit above the fourth layer (including applications that use HTTP), to create client-server or point-to-point communication with each other.
Once the communication is established, HTTP now swings into action to transmit the data. The TCP or UDP manages the communication by ensuring it runs smoothly, and once the data transmission ceases, these layer 4 protocols close the communication. Notably, TCP and UDP use port numbers to identify the web applications that are ‘talking’ with each other. Another point of note is that the implementation of HTTP/3, the latest version, uses QUIC instead of TCP for the transport layer aspect of communication. (QUIC is a multiplexed transport protocol implemented on UDP.)
History of HTTP
HTTP was first released in 1991 following about two years of development by Tim Berners-Lee and his team. Since then, the protocol has undergone an evolution that has seen numerous changes and improvements, leading to several HTTP versions. These versions include:
- HTTP/0.9 (introduced in 1991)
- HTTP/1.0 (standardized in 1996)
- HTTP/1.1 (introduced and standardized in 1997)
- HTTP/2 (standardized in 2015)
- HTTP/3 (introduced in 2022)
What is HTTPS?
While HTTP is a popular protocol that is widely used on the internet, it has a few shortfalls, chief among them security. With HTTP, all information is transmitted in clear text. It can, therefore, be easily viewed by attackers. It can, in fact, be concerning if the data contains sensitive data such as credit card information, passwords, usernames, phone numbers, social security numbers, address details, and more. To solve the security conundrum, HTTPS was introduced.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is a secure HTTP protocol that encrypts all data transmitted via HTTP. HTTPS uses either the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol to validate the identity of the web server and protect the data. The SSL uses keys (public and private keys) and digital certificates to secure the data, while TLS relies on cryptography to encrypt the data. TLS also authenticates both the client and server.
History of HTTPS
HTTPS was created in 1994. At that time, it primarily used SSL. However, later in 2000, HTTPS that uses TLS was standardized. According to observers, it has taken years for TLS to become widely used outside of credit card payments. This is particularly because TLS certificates require additional technical knowledge to install and cost money. As a result, they were not feasible, especially for smaller sites. But the landscape has changed, with web hosting services and cloud companies launching free encryption certificate programs and offering HTTPS for free. By 2017, half of the web was encrypted.
With the basics out of the way, let us now focus on what an HTTP proxy is and what an HTTPS proxy is, their similarities and differences, and their uses.
What is an HTTP Proxy?
Before explaining what an HTTP proxy is, let’s first understand what is a proxy server. A proxy server or proxy is an intermediary that sits between a web client and a web server. It works by routing internet traffic through itself and, in the process, acts as the originator of requests and terminator of responses. Generally, there are a number of proxy servers, each designed to serve a specific function.
In fact, there are proxies configured to act on behalf of the client such that they are perceived as the originators of requests and terminators of responses. Such proxies are known as forward proxies. On the other hand, some proxies can be configured to act on behalf of the server. In executing this role, they appear to be the point at which the requests terminate and the responses originate. Such proxies are known as reverse proxies. Incidentally, HTTP proxies can act as either forward proxies or reverse proxies, depending on the location at which the configuration occurs.
So, what is an HTTP proxy server? It is a proxy server that only routes HTTP traffic through itself. The HTTP proxy is a type of protocol-based proxy alongside SOCKS5 proxies. However, unlike the SOCKS5 proxy, which is essentially meant to facilitate communication through a firewall, the HTTP proxy is intended to act as a high-performance content filter.
The HTTP proxy normally listens to HTTP traffic through ports 80, 8080, 8008, and 3128. It can also listen to HTTPS traffic via port 3129. While it is mostly used in isolation, you can connect it to an existing proxy, particularly if the application you are configuring is already using a proxy server. This arrangement creates a chained proxy.
Types of HTTP Proxies
There are two types of HTTP proxies, namely:
1. HTTP Client Proxy
Typically, an HTTP client proxy forward requests to itself (as an intermediary) before forwarding them to a server or target destination. It, therefore, appears as the originator of the requests.
An HTTP client proxy routes all outgoing HTTP requests and incoming HTTP responses through itself. In the process, it interprets all the contents of the HTTP request and response. It can also change certain contents of the HTTP request as long as they conform to the Guidelines for Web Content Transformation Proxies. Generally, HTTP client proxies change specific HTTP headers, including user-agent, accept, accept-charset, accept-encoding, accept-language, x-forwarded-for, and via. It can also convert the request method from HEAD to GET and vice versa.
Configuring your system and, by extension, web browser to use an HTTP client proxy (more on this below) does a few things. First, it changes the TCP endpoint (port and hostname) in the HTTP URLs to the one that belongs to the HTTP proxy provider. As a result, a TCP connection is first made to a different port and host (the proxy’s port and host) other than the one in the HTTP URLs before being sent to the original/real host and port. This is because the proxy does not alter the contents of the message, which contains the real host and port. As a result, an HTTP proxy can receive requests on a single port before then forwarding the requests and the messages therein to different servers and websites based on the destination data contained in the HTTP messages.
2. HTTP Server Proxy
In some cases, some applications, such as those found on a web server, cannot be configured as originators and instead have to be configured as endpoints. As a result, they appear to web clients as the destination of the requests. When these applications are configured as endpoints, they are known as HTTP server proxies.
Types of HTTP Proxies Ranked by Anonymity
HTTP proxies differ in the degree of anonymity. The following types of HTTP proxies can be distinguished:
- Transparent proxies: With transparent proxies, the user usually does not notice that he is using a proxy connection. The proxy connection is only visible to the website operator or service provider. The main advantage of transparent proxies is that they increase the connection speed by caching data.
- Anonymous proxies: With anonymous proxies your IP address is hidden. In this case, the target website can see that you are using a proxy, but not your actual IP address.
- Distorting proxies: A proxy server of this type can be identified as a proxy by a target web site, but will communicate an incorrect IP address.
- Elite Proxies: These are anonymous proxies that delete user data before the proxy attempts to connect to the target website. With these types of proxies, the target website cannot detect that a proxy is being used, nor can it identify the user’s IP address.
All reputable proxy providers that have HTTP proxies offer only elite proxies.
How to Set Up an HTTP Proxy
This section will primarily focus on how to create an HTTP client proxy. It is created by configuring a web client (browser) to route HTTP traffic through an intermediary. However, it is worth noting that Chrome, Safari, Mozilla Firefox, and other popular browsers do not have in-app (native) proxy server settings.
Instead, when you click on the program’s settings and choose the proxy option, it redirects you to the Windows, macOS, or Linux proxy configuration window. In this regard, to create an HTTP proxy, simply configure your operating system. Doing so will create a system-wide HTTP proxy that works with all other web apps, not just your preferred browser.
To set up an HTTP proxy on Windows, follow the procedure below:
- Open Windows’ Settings > Select Network & Internet > Choose the Proxy tab. Alternatively, you can use your browser to open the Proxy tab.
- Head to the Manual proxy setup section
- On the address field, enter the IP or address of the proxy host. In addition, enter the proxy port. Your proxy provider should furnish you with the details.
- Under the ‘Use the proxy server except for addresses that start with the following entries’ box, enter the URL of your proxy service provider
- Next, check the Don’t use the proxy server for local (intranet) addresses
- Click Save
To set up an HTTP proxy on macOS, here are the steps to follow:
- Click System Preferences > Choose Network > Click on Advanced > Select the Proxies tab. Alternatively, you can use your web client, which will automatically open the Proxies tab
- Next, toggle the Web Proxy (HTTP) option
- Enter the IP and port of the Web Server Proxy (HTTP proxy). Typically, you should enter your proxy service provider’s IP and enter ports 80, 8080, or 8008 in the field.
- Key in the username and password of the HTTP proxy. The username and password should be the same as the credentials you use to access the account you have with your service provider.
- Click OK.
If security is a central consideration when browsing the web, then the HTTP proxy is not ideal. What you would ideally be looking for is an HTTPS proxy.
What is an HTTPS Proxy?
Also known as an SSL proxy, an HTTPS proxy is an intermediary that only listens to HTTPS traffic on port 443. As a result, it only routes HTTPS traffic through itself. As stated above, HTTPS encrypts the data transmitted through the protocol. This effectively means that all elements of the HTTP requests and responses, including the headers and messages, are hidden behind a cryptographic key. Therefore, they can only be viewed or interpreted at the endpoint or point of termination. For an intermediary, such as an HTTPS proxy, to interpret the data, it must be configured as an endpoint.
In this regard, an HTTPS proxy is configured to act as an endpoint of a TLS or SSL connection. It, therefore, decrypts the requests, interprets the contents, changes certain aspects of the requests, encrypts them, and, finally, forwards them to the real destination contained in the HTTP message. As stated earlier, the HTTPS protocol uses certificates. Accordingly, the HTTPS proxy must encrypt the traffic with the correct certificate (either client or server certificate) before sending it to the intended destination. Notably, if the HTTPS proxy is not configured as an endpoint, it should not alter the contents of the HTTP header or request, as stipulated by the Guidelines for Web Content Transformation Proxies.
HTTPS proxies are generally used to secure web servers or web clients by performing encryption.
Types of HTTPS Proxy
There are two types of HTTPS proxies:
1. HTTPS Client Proxy
An HTTPS client proxy facilitates connections from a web client or internal network to the internet. To set up an HTTPS client proxy, you must import a client certificate for use by the device on which the proxy is installed. This enables the intermediary to both decrypt and encrypt data as if it were the originator of the requests or terminator of the responses.
2. HTTPS Server Proxy
An HTTPS server proxy allows connections from external web clients to internal web servers via the internet. An HTTPS server proxy differs from an HTTP server proxy because the former utilizes certificates, while the latter does not. To set up an HTTPS server proxy, it is important to export the default certificate used by your web server to the proxy. The certificate enables the HTTPS server proxy to encrypt and decrypt the data.
How to Set Up an HTTPS Proxy
Setting up an HTTPS proxy follows the procedures detailed above, with only slight differences around the ports used. Always ensure you have entered 443 within the port field every time you are creating an HTTPS proxy. If you are using a macOS device, do note that you must select the Secure Web Proxy (HTTPS) option instead of Web Proxy (HTTP). Otherwise, the procedure is largely the same.
How Secure is a Connection Through an HTTPS Proxy?
When a user using an HTTPS proxy opens a web page with a “lock icon” to the left of the address bar, the entire connection between the user’s browser and the server of the target site is encrypted (SSL encryption):
This means that all data entered by the user on the keyboard (logins and passwords, credit card numbers, etc.), images, and videos downloaded, uploaded, or streamed remain absolutely private.
Browser HTTPS-Proxy Target page
This means that they are known only to the user and the owner of the target website.
Can the Proxy Service “Listen” to the Traffic?
No, this is technically impossible. The proxy provider can only guess that the user is trying to hack passwords to accounts on any website. This is apparent from the frequency of access to the login page of the target site. This will occur if the user does this at a frequency of one million times per minute using a brute force program.
HTTP Proxies vs. HTTPS Proxies: Similarities and Differences
Similarities Between HTTP and HTTPS Proxies
- They can be configured on either the client-side or server-side
- HTTP and HTTPS proxies interpret the data transmitted through them
- The proxies listen to traffic via ports
- Client-side proxies forward all requests to the target destination
- Client-side proxies can be used to facilitate web scraping
Differences Between HTTP and HTTPS Proxies
HTTP Proxies
HTTPS Proxies
Ports
They use ports 80, 8080, 8008, 3128, or 3129
They use port 443
Security
HTTP proxies route unencrypted data
HTTPS proxies route encrypted data
Protocol
They mainly use the HTTP protocol
They primarily use the HTTPS protocol
Traffic
They can listen to both HTTP (via ports 80, 8080, 8008, 3128) and HTTPS traffic (via port 3129)
They can only listen to HTTPS traffic via port 443
Uses of HTTP and HTTPS Proxies
Uses of HTTP Client Proxies and HTTPS Client Proxies
1. Web Scraping
Web scraping refers to the automated process of extracting data from websites using bots known as web scrapers. Ordinarily, these bots are designed to extract large volumes of data, which can strain web servers by unnecessarily usurping resources. For this reason, most large websites are now implementing anti-scraping measures aimed at stopping any data extraction efforts. Fortunately, you can get around this problem using HTTP proxies.
HTTP proxies are mostly overlooked when it comes to data extraction. This is because residential proxies, mobile proxies, or data center proxies are preferred as they mask the IP address of the computer on which the scraper is running. It simultaneously assigns a different IP address, effectively providing online anonymity. Additionally, it protects the real IP address from getting blocked or banned. If the IP address is rotated periodically, the chances of blocking are further reduced. But this article isn’t about residential or data center proxies. So, how are HTTP proxies and HTTPS proxies used in web scraping?
As stated, an HTTP or HTTPS proxy can change some HTTP request headers. These include the user-agent, accept-language, accept-encoding, and accept, just to mention a few. The user-agent stores information about your operating system (type and version), the client application in use (web browser), and the browser engine. This information allows a web server to identify the type of device and software used to access it. It then uses this information to create an online identity associated with the user. By altering the user-agent, an HTTP proxy and HTTPS proxy can make it appear as though the requests are originating from different devices. This boosts web scraping, as the data extraction requests appear to have been sent by multiple devices.
2. Content Filtration
An HTTP client proxy or HTTPS client proxy can be configured to forward only specific requests – such requests must fulfill certain rules. For instance, they must be sent through specified ports. Access is denied if the HTTP client uses a port other than 80, 8080, 8008, 3128, or 3129.
Additionally, you have to specify the types of content the HTTPS or HTTP proxy should look at as it examines traffic to and from a client. The traffic is blocked if the content does not match the criteria specified in the settings. Conversely, if the content matches, then it is allowed to pass through the intermediary.
3. Securing Communication
An HTTP proxy can be configured to convert the inbound data from plain text to secure, encrypted outbound data that can be accepted by HTTPS servers. However, this configuration is unusual, but it involves the use of port 3130, which is the port that handles plain text to SSL communication.
On the other hand, HTTPS proxies secure communication by encrypting it. In this way, HTTPS proxies promote cybersecurity, as they reduce the chances of cyberattacks.
4. Social Media Management
By now, it is common knowledge that HTTP proxies modify some aspects of the HTTP header. Thus, by changing the user-agent, these intermediaries can create the illusion that the requests are originating from different devices.
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/what-are-http-and-https-proxies/
Montag, 27. Mai 2024
How a mobile proxy service works
Mobile proxies are used exclusively from cell phones. The user is given access to an IP address, which serves as an intermediate level to which the data traffic is first routed. Unlike conventional proxies, which use broadband cable or WLAN connections for data transmission, mobile proxies use mobile data networks.
The term "mobile proxy provider" refers to two completely different business models.
1. The first model is the so-called residential proxies, which are hosted on devices of uninformed third parties. These can be mobile, but also stationary devices. Residential proxies are unstable and only work as long as the respective owner is online.
2. Another model that is currently in vogue is the purchase of cell phones or modems and SIM cards from one or more mobile operators. Such a "mobile proxy farm" offers the chance to share the costs of proxy use among many people. The usage price is usually based on the number of IP addresses included. Alternatively, a dedicated IP address with unlimited traffic and its own API management can be rented.
Use of a mobile proxy service from the customer's point of view
The basic principle of the mobile proxy service is approximately the same as that of a conventional proxy service (residential proxy service). The customer receives the so-called gateway IP address with a non-standard port that looks something like this:
123.123.123.123:54321
This data must be entered in the browser or bot settings. The customer then receives the IP address that corresponds to the profile settings. Contrary to residential proxy services, the selection of mobile operators and available countries for mobile proxy services is much narrower.
Advantages of mobile proxy services
Mobile IP addresses are considered particularly trustworthy. The main reason for this is that the so-called GNAT technology (short for "GPRS Network Address Translation") is used here.
Also, each proxy is a unique device that is equipped with a separate SIM. Furthermore, mobile proxies are very fast proxies, which guarantee high running stability.
Another advantage of a mobile proxy server is that the hardware used is controlled by the mobile proxy service. The software is also controlled by the used service. Any major mobile platform, be it Android or iOS, can be emulated.
Application areas of mobile proxies
In principle, mobile proxy services are accessible to everyone. A possible field of application in the private sector is price comparison. For many internet sellers, the displayed price depends on the current location of the user. However, if a mobile proxy server is used, the actual price can be determined without blocking the user.
However, the use of mobile proxies only makes economic sense in the commercial sector - for example in the context of marketing campaigns on portals such as Instagram, Tik Tok, or Facebook. Mobile proxy servers are mainly used for the verification of links and ads. Mobile proxy servers are also ideal for ad verification, SERP and market research.
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/what-are-mobile-proxies/
Sonntag, 26. Mai 2024
Where do such proxies come from?
A proxy provider buys so-called "installations" from software developers (free games, add-ons, etc.). In other words, the proxy provider negotiates with programmers of free applications and offers to monetize their applications by integrating the code of the proxy server, i.e. the proxy software, into their source code.
A user who has downloaded a corresponding application agrees during installation that resources of his device may be used by third parties. As soon as he accesses the Internet, the IP of his device is added to the pool of the proxy provider and is available to customers of the proxy service as a proxy.
Are residential proxies legal?
Yes, at least large proxy providers operate legally (though only after a series of scandals). This means that today, if a user downloads a free program or installs an add-on in his browser, he agrees to the TOS (Terms of Service) conditions - although these are usually not actually read.
What are the options for users of a residential proxy service?
The user area allows the user of a residential proxy service to customize the following parameters:
- Create a separate profile for a specific country, state, city
- Select ideally suited internet providers
- Select the IP type he wants to have at the output (mobile or desktop)
- Select the IP change frequency. For example, to have the IP change each time the page is reloaded, or to save an IP as long as possible (so-called sticky IP), but in reality, it does not take more than a few minutes.
After completing the profile settings, the customer receives a so-called gateway IP address with a non-standard port that looks something like this:
123.123.123.123:54321
In this case, 123.123.123.123 - is the IP address of the proxy service, which is the same for all its clients, and 54321 is the port where the client gets the output IP addresses corresponding to the settings of the created profile.
How to use such a gateway IP?
All one needs to do is to enter the gateway IP into the network settings of their browser or bot, and the connection will run through the devices defined in your profile - e.g. only a mobile connection and only residents of North Rhine-Westphalia who solely use Vodafone service provider - with a certain frequency of change (e.g. every time the client of the proxy service reloads the page of their browser, they will receive an IP address of a new device that corresponds to the settings of the created profile).
Advantages of residential Proxies
- Low probability of blocking on a target page
- The IP pool of the large residential proxy providers contains a huge number of proxies (10+ million) - there are always suitable proxies to choose from
- Flexible API (application programming interface) settings; the ability to create multiple profiles for different geo-sites, etc
- Accurate geo-targeting (up to a specific city)
- Choice between desktop and mobile device
- Selection of a specific internet provider (Vodafone, T-Mobile, etc.)
Disadvantages of residential proxies
- Unstable speed, connection breaks
- Impossible to keep a certain IP for more than 30 minutes (max.)
- Customer of the proxy service must pay the traffic volume separately
When are residential proxies used?
Residential proxies are always useful when working with websites that have strong antibot protection and geo-dependent output: postings in Craigslist, parsing of regional Google editions (SERPs), analysis of product placement on amazon.com, booking.com, etc.
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/what-are-residential-proxies/
Samstag, 25. Mai 2024
Where do proxy services get such proxies?
Proxy services that sell access to proxies hosted in data centers are usually IT companies (usually hosting companies) that can buy or rent large blocks of IP addresses (IP subnets) from various LIRs (Local internet Registry, i.e. official registrar organizations) and have many powerful servers in data centers around the world.
An example:
A proxy provider buys a subnet 175.123.123.0 - 175.123.123.255 (a fictional example, just for clarification) from an American registrar. He then rents servers in data centers in Dallas and New York and installs proxy software on them.
He does the same with the subnet 185.123.123.0 - 185.123.123.255 by buying or renting it from a German registrar and installing proxy software in data centers in Frankfurt and Berlin.
This process is repeated in Russia, Singapore, Brazil, etc. Large proxy services can have hundreds of such subnets.
What is the purpose of this?
A proxy service offers its customers access to these proxy servers against payment. The goal of the customers in turn is to change/replace/hide their real IP addresses.
The procedure is as follows: The customer buys access to the service, receives a list of the IP addresses available to him and uses them by entering them into his browser settings, bot, etc.
Why are data center proxies so popular?
- The IPs of such proxies do not change (permanent IPs), i.e. as long as the customer pays the rent for the IPs, he can be sure that his IP will not suddenly change.
- High data transfer rate and high availability (uptime), as well as a wide channel and constant network monitoring by data center staff and the proxy team. Malfunctions and short shutdowns of these proxies do occur, but are more of an exception. Usually they are caused by very rare software updates or short maintenance interruptions (thermocouple replacement, hard disk failure, etc.).
- No traffic restrictions. The price and amount of IPs that the buyer sees before making a purchase does not change. This means he knows how many proxies he will get and can be sure that he does not have to calculate in advance how much traffic will be routed through these proxies. The functionality of the proxies purchased will not be affected if any traffic limits are exceeded.
Data center proxies are ideal for long-term marketing campaigns, such as an increased presence of start-ups in social networks (Facebook, Instagram, etc.). When someone creates a completely new account on a social network and the subscriber base is gradually expanding, it is very important that the account is managed from the same IP address. This increases the trust of the social network and reduces the probability that anti-spam mechanisms are used and the account is blocked.
What are the disadvantages of data center proxies?
The disadvantage of data center proxies is their IP addresses. If you run a WHOIS check on such an IP, you will notice that it is registered to an IT company (e.g. web hosting) and not to a private or mobile internet provider.
In some cases this criterion can be used as a filter and this proxy will not work on certain pages. An example is the block of data center proxies on Nike's and Adidas' websites for sales of limited sneakers.
Services that provide access to this type of proxy have full control over the hardware and software part of the proxy and regularly "renew" their IP sub-networks, gradually taking them out of service and replacing them with new ones.
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/what-are-data-center-proxies/
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/understanding-rotating-proxies-essential-guide-alexander-schmidt-0tpmc
Freitag, 24. Mai 2024
Where do public proxies come from?
Public proxies can come from different sources.
First example: An inexperienced server administrator (e.g. an administrator in an educational institution) installs a proxy script for the institution's requirements, but does not change the default ports (80, 3128) and does not secure them with a password. In this case the institution's server becomes a public proxy.
Second example: An Internet user downloads a program that contains a security hole and cannot be updated because the copy protection has been removed ("cracked software") or a Trojan has been installed. In this case the private computer becomes a public proxy.
All these servers and private computers are now accessible from the outside. This means that if you know their IPs and the port where the proxy is open, this remote computer can fulfill the function of a proxy, i.e. you can send and receive requests to other servers through it.
Where free proxies originate
The ranges of IP addresses are scanned using programs like Charon, usually from similarly infected servers. Attention: This is illegal and there may be legal consequences for such activities. The IP addresses are then used to send spam via SMTP ports as well as for brute force and DDoS attacks.
After such proxies become unusable (i.e. when their IPs are added to the spam database), they are often published in unrestricted forums.
It is strongly discouraged to use such proxies to transfer important data: e.g. for social networks, instant messengers and especially to conduct financial transactions.
Who uses public proxies?
Despite all the risks associated with the use of public proxies, they are in great demand among SEO specialists. Because usually Google does not manage to block them and they can be used to parse search results.
You can find a list of such proxies on the page with free proxies.
However, there are also online services that offer lists of IP addresses for money. These proxies are usually collected with the help of parsers in well-known proxy forums and other websites.
Prior to the sale, the list is checked for duplicates and availability, sorted by geo-location and protocol and sent to the customer.
Disadvantages of free proxy lists
Potential buyers of such lists should be aware that services offering such lists have no control over the listed proxy servers. It is impossible to check for which purposes and by how many people such proxies have already been used.
Such proxies typically do not have a long "life span" ̶ usually until the server administrator or computer owner notices an unusually high load and closes the security hole (or simply reinstalls the system).
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/what-are-free-or-public-proxies/
Donnerstag, 23. Mai 2024
As a result, many companies are faced with far-reaching decisions. On the one hand, the sensitive company data must be protected, on the other hand, the entrepreneur wants to benefit from the diverse services of the internet.
This is where the proxy server comes into play. It protects your company from internet attacks, because the proxy server is located between your own computer and the web server where the content of the website to be opened is stored. This means that all requests go through it.
What is important when choosing a proxy server?
The choice of proxy server is a strategic decision for companies. Proxy servers on the internet have different security standards. The security levels are divided into low, medium and high. Only a proxy server with a high security level hides the IP address so well that anonymous surfing is possible.
Free proxy servers should be used with caution. A study by IT expert Christian Haschek revealed that of 443 proxy servers examined, only 199 were online. The remaining 244 servers were offline. Of the accessible 199 proxy servers, 79% forced the requested websites to switch from the secure HTTPS protocol to the insecure HTTP procedure. This forced conversion enables providers to read data entered theoretically, such as passwords, in plain text. Christian Haschek also found out that every fourth proxy server modifies either the HTML code or the JavaScript elements. These modifications allow malware to be distributed in addition to advertising.
These risks can lead to further problems and result in mass blocking ("bans") of accounts (e.g. in social media). Among other things, this can lead to considerable damage to the image of the company in question and consequently to economic losses. In addition, insecure proxies can easily allow sensitive or private data to be tapped by the provider or malware. The choice of the proxy server should therefore be well thought through.
What are the characteristics of good proxy servers?
If you decide to use a high quality proxy server, you have several advantages. The provider delivers the IP addresses within seconds. The security standard is based on current technology and is high accordingly. Most proxy providers give their customers a money-back guarantee that is valid for a certain period of time. Good proxy servers run reliably, support data protection and offer higher performance.
The risk that the server is not accessible is usually extremely low. There is a technical customer service available 24/7 at most proxy server providers. Especially medium and small companies should play it safe. Protect your network and your data with a good and secure proxy server.
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/why-is-choosing-the-right-proxy-server-so-important/
Mittwoch, 22. Mai 2024
Proxy server to simulate DDoS attacks
Every company is required to protect the data of its internal IT systems. In order to check the extent to which a company's IT infrastructure is secure, certain tests can be carried out - simulations of so-called DDoS attacks.
With a simulation of DDoS (short for Distributed Denial of Service) attacks with real IPs, systems can be tested for their resilience. In the process, a large number of targeted requests are made from numerous computers, which can lead to a server overload and paralyze services provided by the attacked party.
With such simulated attacks, important data can be obtained about the extent to which the sensitive IT system can withstand an attack and where the system needs to be further expanded in the area of cybersecurity so that important company data cannot be hacked.
Network and website monitoring
Especially in marketing, network and website monitoring is an important task and an integral part when analyzing how to make marketing strategies successful.
With proxies, marketing professionals can check how users from all regions of the world are using the site or even an app and how the service is performing. Using proxies, the region from which the website, app or network is accessed can be adjusted simply by changing the IP address, making it easy to see how a website can be accessed from different regions.
Is all content displayed? Is the loading time of the website fast? These important questions can be easily checked by this method; it will reveal where improvements are necessary.
Protection of company data
Proxy servers play a major role in protecting a company's internal data. Even small companies have to ensure that their IT systems are shielded against external attacks and data leaks are prevented by an adequate security system.
They are placed between the attacker's own system and any external access, thus acting as an extra hurdle that prevents the attacker from accessing the IT system directly.
In addition, proxy servers provide a certain degree of anonymity when surfing the internet and disguise your IP address. A new IP address is generated by the proxy server, and thus your own, real IP address is not revealed.
In addition, in many companies nowadays, it is quite common for employees to work from home, which presents new security risks for company data, as it is not always possible to ensure that employees' internet connection is secure. By using proxy servers, the risk can be minimized and the company data can be protected.
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/why-cybersecurity-professionals-need-proxies/
Dienstag, 21. Mai 2024
Market research
Collecting and analyzing the information needed to create a marketing strategy can be a challenge.
Many companies take steps to protect their websites from IP addresses of certain companies. Sometimes the only solution is to use a proxy server to collect data on the internet.
Web scraping
Web scraping automatically reads large amounts of data from websites. Most popular websites actively protect their resources from web scraping by using IP address detection, HTTP request header checking, CAPTCHAs and other methods.
It is unlikely that a real user can request 20 pages per second on the same website. To prevent the web server from responding and blocking your requests, you can indicate that all these requests come from different locations. In other words, using a proxy is helpful here. Free proxies are less suitable for such purposes: They are often slow and unreliable.
Verification of advertisements
Many users use various tools to fake ad traffic, resulting in a large number of ads that are never seen by real users.
Therefore, more and more companies are using proxy servers to detect such behavior. In this case, using a proxy server increases the effectiveness of advertising and makes it possible to anonymously check the target pages of advertisers.
Price comparison
Companies that offer goods and services on the internet set the prices for their products in comparison to those of their competitors in order to be one step ahead of the latter. Therefore, price comparison is an important part of daily business.
However, some websites track these activities and are able to detect when competitors access their own website. They automatically provide false information to maintain competitive pricing.
Using a proxy, you can capture an unlimited amount of the most accurate data available. By giving websites access to the actual IP addresses of visitors, you are perceived as a buyer, not a competitor, and can collect accurate pricing information.
SEO monitoring
A website audit, i.e. a review of your website in terms of SEO (Search Engine Optimization) figures, provides you with information about what you need to fix and what measures you can take to improve your website's search engine rankings.
Effective SEO monitoring, i.e. the constant monitoring of websites in terms of SEO key figures, requires a more in-depth analysis, which is often detected and blocked by websites.
Proxy servers are useful for the correct collection of usage data. Many proxy providers have over 50 million IP addresses of home users worldwide, which can help you perform SEO monitoring more efficiently.
Promotion on social media
SMM advertising is a whole complex of activities to promote a group or a specific profile. However, restrictions on social networks, for example, in terms of the daily number of friends added or messages sent, significantly slow down the process of increasing the popularity of a company.
Social networks monitor IP addresses and block particularly eager users. Therefore, SMM advertising requires the use of alternative access methods such as proxy servers.
SMM promotion managers often use special software that can manage several dozen or even hundreds of accounts at the same time, so from the outside it looks like a real person is using the site. However, for such programs to operate effectively, they require the same number of access points as profiles. The way out of this situation is to use stable proxy servers.
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/why-do-online-businesses-need-proxies/
Montag, 20. Mai 2024
Over the years, a large community has developed on Ebay based solely on buying goods at a low price and then selling them for a higher price. To improve the efficiency of these sales, users often use support software. Usually Ebay allows the use of such software.
However, sometimes an Ebay account may be suspended due to a violation of the rules. For Ebay it is important that all users are real people or companies with real goods and real buyers of those goods.
The attempt to sell or buy too many items at once alone, as well as other rule violations, can lead to the loss of an Ebay account and legal repercussions.
Why do Ebay users need proxies?
The use of proxy servers helps to avoid Ebay-blocks. A frequent reason for a ban on Ebay is the regular access to an account from different IP addresses. That is why it is recommended not to use more than two proxies for one Ebay account.
Sneaker copping
Online stores that offer sneakers often have anti-spam systems to detect unusual buyer behavior. On such sites, you can often only have one account and buy one pair of sneakers per account. Consequently, sneaker resellers need to create many accounts in order to buy the number of sneakers they need.
That means they have to create other accounts with different email addresses, credit card information and shipping details. None of this will help if you use the same computer to manage all these accounts.
Sneaker websites can identify this computer through its IP address. This is where proxies come into play. They help to disguise the real IP address so that several accounts can be created in an online sneaker store and managed from one PC.
Gamers need proxies as well
Online games are more popular today than ever. Gamers, i.e. users of online games, do not need to download and install special applications. All they have to do is register and log on to the corresponding provider website. In some situations, however, it doesn't work without personal proxies.
Proxy server functions for online games
Proxies act as intermediaries between your computer and the web resource you want to access. Proxy servers help to hide your actual location, i.e. your IP address, and replace it with another IP address.
This is always useful when gamers want to play on websites that are blocked in their region. Using a proxy from a different, unblocked country can work around this problem.
By purchasing proxies, you can also easily perform the following actions:
- Creation and maintenance of multiple player accounts
- Effective recording of game data
- Secure input of personal data
Anonymous proxies are essential if you want to protect your account or personal information against hackers.
In addition, the ping can be significantly reduced (up to 3 times) with a proxy. "Ping" is the time span needed for data to be transferred from your PC to the server. The lower the value, the faster the gamer sees his opponent's reaction and can react more efficiently. In online games today, immediate reaction can mean the difference between victory and defeat.
Bypass workplace locks
Another option for using proxy servers is to bypass local restrictions at workplaces or educational institutions.
Managers of large companies often try to control the (effectiveness of the) work of their employees by blocking access to entertainment portals (including game portals) on office computers.
With proxies, you can pursue your favorite pastime at any time, while information about the web resources you visit is inaccessible to your ISP and employer.
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/why-do-online-shoppers-and-gamers-need-proxies/
https://youtu.be/cbzBS1r9oW4
Sonntag, 19. Mai 2024
Why does the IP address have to be hidden?
On Netflix, YouTube and other websites, certain content is only accessible to users from certain countries. Other websites such as LinkedIn are completely blocked in certain countries.
To ensure that users from "blocked countries" can see corresponding content or websites, they must "pretend" to the provider that they come from the "allowed" country. This can be achieved quite easily by using proxies.
Twitter and Facebook
Social networks such as Twitter and Facebook also block access to their content from different countries ̶ or these services are blocked in certain countries. For example, North Korea, Iran, China and many other countries force internet providers to block access to Twitter and/or Facebook.
The reasons for this are complex: many governments, especially in the Middle East and Asia, control information online for their citizens and want to stop the exchange (in a political context).
But also companies and schools often block access to social media sites in their internal networks. The main reasons cited are reduced productivity and an increase in the likelihood of cyberbullying and distraction.
However, Twitter and Facebook are not only used for personal purposes – many companies use these social media platforms as a marketing tool for communication with followers.
One and the same user therefore often manages many different accounts and/or company pages on Facebook/Twitter, which they usually try to block. With proxies these restrictions can be overcome. Proxies are therefore extremely useful for those who do online marketing on a large scale.
Proxies with Torrents
Torrents use a file-sharing programme such as BitTorrent, uTorrent or Vuze to download content (usually popular and therefore usually legally protected films, music, software, etc.) to your own computer.
However, data is also uploaded from your own computer and thus shared. In most countries this is prohibited, so users who download/sharing illegal content are liable to prosecution.
When you download/share a torrent, you connect to a variety of other users (also called a swarm). All users in the swarm can see the IP address of your machine. These often include monitoring groups paid by the entertainment industry to identify users who share illegal content. With the help of the IP address, the internet provider is then informed about the (criminal) activity of his customer and/or legal action is taken.
In order to avoid claims from copyright holders, Torrents also uses proxies, which are also used to hide the user's IP address.
With the help of proxies, blocked or legally protected content can be accessed or downloaded "anonymously" from anywhere. And although proxy services do not approve of this, they cannot technically restrict it. Only after requests from copyright holders are received will accounts of such users be blocked.
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/why-do-private-users-need-proxies/
Samstag, 18. Mai 2024
The total number of IP addresses to which such a proxy service has access is called an IP pool. With the many companies that offer proxy servers, it can be difficult to find the right provider. To make the right decision, you should understand the main types of proxy services.
What types of proxy services are there?
There are different types of proxy services, which determine the level of efficiency and the cost of the service:
Services that offer free proxy lists. Here the user only needs to copy one of the IP addresses given in the corresponding list into his browser settings. The big problem here is security, because almost none of these "free servers" reliably hides the IP address of the user. In addition, many servers of this type are offline („dead Proxies“), they use the insecure HTTP procedure and process the HTML code of websites, which can lead to the spread of advertising and malware.
Services that provide access to data center hosted proxies are the most common type of proxy service. Among these, ProxyCompass stands as a prime example, offering access to data center hosted proxies. IP addresses of servers in data centres, such as those provided by such services, are popular mainly because of their speed. This unparalleled velocity enables many users to complete their tasks before they are discovered by websites. With ProxyCompass und similar services, clients can take advantage of these swift, efficient, and secure proxies, tailored to meet various demands.
Residential proxies. These are IP addresses of private homes, which you can use to forward your requests via the "home network". These IP addresses are more difficult to obtain, making them considerably more expensive than data centre proxy server addresses. The use of such IPs raises legal and compliance issues because they use private networks of individuals.
Mobile proxies. These are IP addresses of private mobile devices. Obtaining IP addresses from mobile devices is quite difficult, which is why they are among the most expensive proxies. For most web scraping projects, mobile IP addresses are not required unless you want to analyze the results displayed to mobile users. These proxies pose even more complex legal and authorization problems, as the owner of the device often does not fully recognize that you are using his GSM network.
Why would you need Proxies?
If you work in a large SEO research company where many computers use the same IP address for keyword analysis, website analysis and other SEO operations, search engines may misinterpret your repeated and relentless visits to the same web address.
This access, which is interpreted as a unusual activity, can lead to you being blacklisted by search engines, i.e. blocked. This risk can be avoided by using a proxy server.
The different purposes of using proxy servers can be divided into several groups:
- Anonymisation: You can hide your IP address via a proxy server so that other members of the network can only see the address and location of the proxy server.
- Filtering: Proxies can also use filters to evaluate incoming requests and thus allow only certain types of requests to pass. This is often the case in corporate networks that block certain services, such as file sharing or gaming websites.
- Caching: Data is temporarily stored in a cache by a proxy server in order to be able to process duplicate requests faster. For example, if a client regularly requests the same document, it can be accessed directly by the proxy without having to connect to the actual target server. This often saves bandwidth and money.
In order to choose the most suitable proxy service for you, you should clearly know your destination. You can find more information about the different types of proxies in the 3rd part of our knowledge base.
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/what-is-a-proxy-service/
Freitag, 17. Mai 2024
Basics of the function
The way it works is based on three essential elements that work closely together to ensure that requests are processed quickly and purposefully:
- IP address
- Port
- Protocol
Every device that can access the internet has its own IP address. This consists of four numerical sequences. Each sequence is separated from the next by a period (e.g. 123.123.123.123).
These sequences of numbers are called octets in technical parlance. Laptops, routers, servers, telephones and numerous other devices, such as printers, have their own address that is connected only to this device. The IP address allows you to find out a geographical location, the provider and much more.
The port can be compared to a door in a house, equating the house with the respective device. Communication with other devices is enabled through the door. The port is set as a numeric value behind the IP address, separated by a colon (e.g. 123.123.123.123 : 8080).
The language of communication between devices is called protocol. It can also be a format. The most important and at the same time best known formats are HTTP and SOCKS. There are also other protocols, but they are rarely used.
Procedure for requests to the proxy server
The Internet user is referred to as the client for such requests. The client sends a request when trying to open an internet page. The IP address of the user is transmitted for identification purposes. The request is sent to the server, which can access the content.
In response, the requested information is sent back to the IP address, i.e. to the PC or other internet-enabled device. However, the proxy server is not the destination server. Therefore, the proxy server can also be seen as a middleman, since it mediates between the internet enabled device and the target server.
Accordingly, the request is made in two moves. In practice, this means that the request is sent to the proxy server with its own IP address. The proxy server then forwards the request with its IP address to the relevant server. In response, the information, i.e. the content of the page, is sent back to the proxy server, which then forwards it to the client.
The location of the proxy server has no influence on its function and concrete procedure. However, the information on the pages varies according to the IP address of the proxy server. Each country has different regulations and restrictions, which are observed accordingly. The communication of the different devices can be different. But the basic procedure remains the same for all devices.
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/how-do-proxy-servers-work/
https://medium.com/@traffic4drive/buy-socks5-usa-42f828a1a6ad
Donnerstag, 16. Mai 2024
Free Proxy List
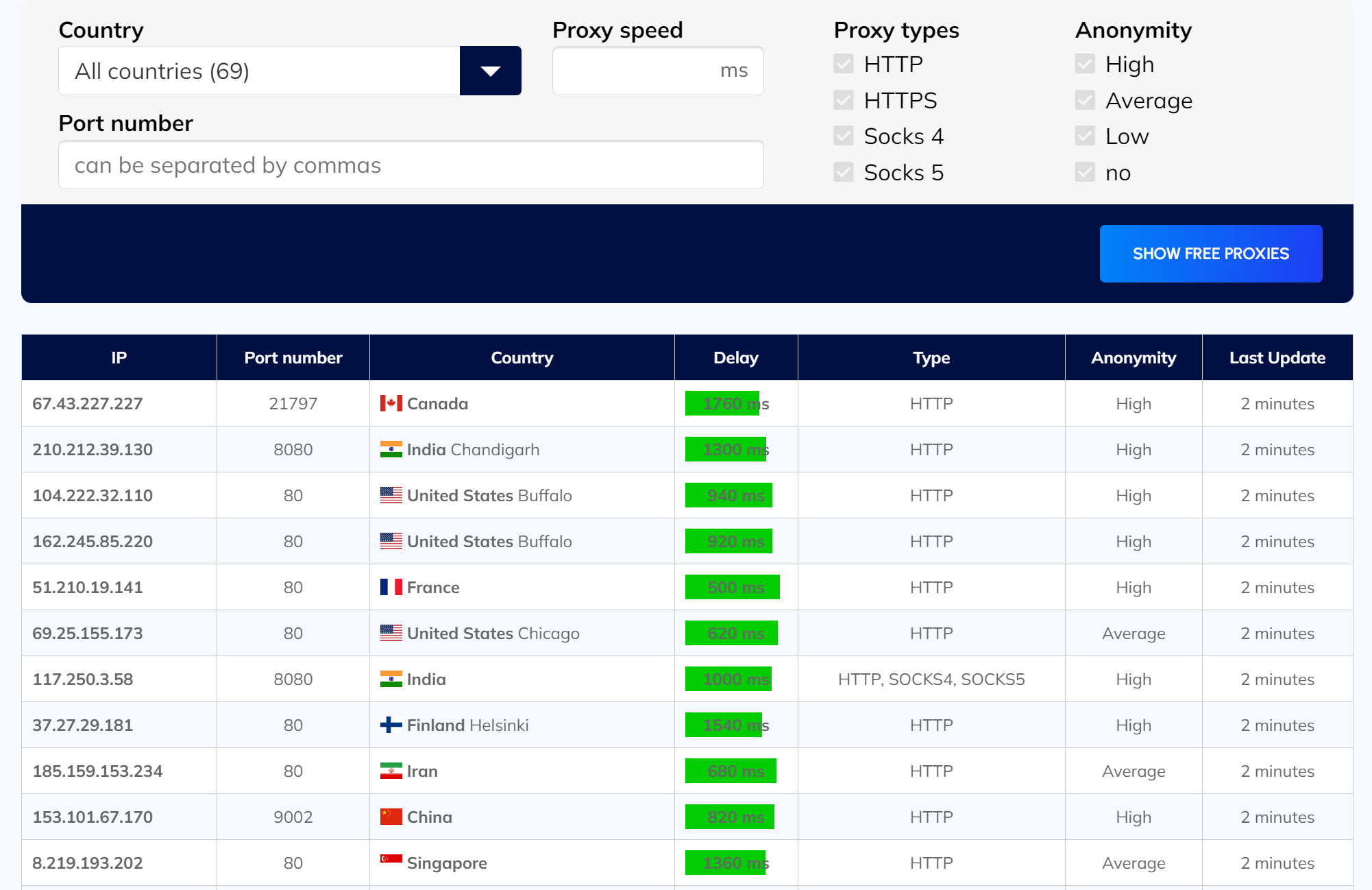
All proxy servers in the list are continuously monitored and sorted based on various parameters.
Here are the different types of proxies:
- HTTP: These are standard proxies that support HTTP requests. They can be used to browse websites and download files using the HTTP protocol.
- HTTPS: Also known as SSL-enabled proxy servers, they allow you to access HTTPS sites securely. They can also be used with specialized programs that support different protocols, such as SOCKS proxy servers.
- Socks 4: These proxies support the SOCKS protocol version 4. They enable connections to any address and port using the TCP/IP protocol.
- Socks 5: These proxies include all the features of version 4, with additional capabilities such as UDP protocol support, DNS requests via a proxy, and the ability to open ports for incoming connections using the BIND method.
Proxy anonymity is a crucial parameter that determines whether your real IP address is hidden and whether the destination server can detect your proxy usage.
Here are the different levels of anonymity explained:
- No Anonymity: The remote server knows both your IP address and that you are using a proxy.
- Low Anonymity: The remote server does not know your IP address but is aware that you are using a proxy.
- Moderate Anonymity: The remote server knows that you are using a proxy and might think it knows your IP, but it is actually not your actual IP (usually seen with multi-network proxies that show the incoming interface as REMOTE_ADDR).
- High Anonymity: The remote server has no knowledge of your IP address and has no direct evidence of you using a proxy. These are anonymous proxies.
The speed of the proxy server is indicated in milliseconds and is not a ping measurement. It represents how quickly a small text file can be uploaded via the proxy. You can easily gauge the speed by observing the color of the stripe: green indicates fast speed, while red indicates slower speed.
Ping may vary, so if it's an important factor for you, it is advisable to check it directly from the device where the proxy will be used.
These free proxies can be used with software applications that support proxy usage, such as web browsers. Popular use cases for proxies include hiding your real IP address, concealing your geographical location, and accessing blocked websites.
If you are looking to purchase fast and reliable proxies located in data centers, supporting both HTTP and SOCKS protocols, you can follow the links below to buy proxies for specific countries:
- Buy China Proxies
- Buy US Proxies
- Buy German Proxies
- Buy UK Proxies
- Buy Russian Proxies
- Buy French Proxies
On the aforementioned pages, you can find and purchase high-quality proxy servers that offer exceptional speed and performance.
https://proxycompass.com/free-proxy/
Get a Free Proxy Trial for 1 Hour
Free Trial Details
- 50 proxy IP addresses
- Static data center hosted
- HTTP(S) and SOCKS4/5 protocols
- US locations
- Unlimited bandwidth
- Full anonymous elite proxies
- Access to the proxies within 5 minutes
- Upgrade to a paid account at any time
What Do You Have to Do to Try These Proxies for Free?
To try these proxies for free, you need to register on our website and send us a message through our ticketing system.
If possible, please specify the target website or the activity for which you need the proxies. We will try to assist you with suitable recommendations.
Need more time to test? Then go to the pricing page, select the proxy package that interests you, and test it risk-free for 24 hours. If you are not satisfied with the results, let us know through our ticketing system. We will give you a full refund.
Free Proxy Server Package
50 proxy IP addresses
After a quick and non-binding registration you will receive a list of 50 IP addresses available for use. Depending on the software you're going to use them in, you can either use them all at once or use them one by one through a special API, which rotates and randomly gives out the IP addresses of proxy servers.
Static Data Center Hosted Proxies
The proxy servers you get for the test are static. This means that their IP addresses never change, i.e. they always remain the same. Physically, these proxy servers are located in different data centers in the U.S. This means that they are always up and running and you can use them at any time of the day or night.
HTTP(S) and SOCKS4/5 Protocols
The proxy servers you get support all popular protocols, i.e. HTTP/S, SOCKS4/5 at the same time.
Inside the user panel you can download your list of proxy servers in any format you need.
USA Locations
This free proxy package contains IP addresses from the United States. The exact number of IP addresses from specific cities in the United States is unknown, as this package is automatically generated.
Unlimited Bandwidth
We do not limit the amount of traffic used by our clients for downloading and uploading. This applies to both paid packages and this free package.
Full Anonymous Elite Proxies
These test proxy servers are exactly the same as our paid proxy servers. They are as anonymous as possible.
Upgrade to a Paid Account at Any Time
Once you have tested the proxy servers for compatibility with your tasks, you can choose any proxy package that suits your needs directly from the user panel.
https://proxycompass.com/free-trial/
The proxy server acts as an intermediary between your computer (client) and the target server, so there is no direct connection between them. This is because the proxy server forwards your request with its own IP address.
Advantages of the Proxy Server
A proxy server offers advantages for both the client, i.e. you as a user, and the target server:
- The proxy server does not inform the target server about the requesting IP address (client). Only the IP address of the proxy server is forwarded. Consequently, the identity and location of the client remain hidden; security is therefore the great advantage for you as a user.
- Proxy servers have a storage capacity. Frequently requested pages are stored on the proxy server and can be transmitted directly back to the client without a new request. This has the effect of saving a little time, which is especially noticeable with a slow Internet connection.
- Since the target server can only be reached externally via the proxy server, the former remains protected from possible attacks; thus, the proxy server acts as a firewall.
- However, the proxy server can also control the content of incoming data packets and block unwanted or illegal content that way, for example.
- If the proxy server is located abroad, the target server receives a request from an IP address from that country. That way, restrictions that only apply to certain countries (e.g. blocked (YouTube) videos or websites) can be partially circumvented.
Rent or buy Proxy Server
There are free proxies for individual users and public proxy servers. Proxy servers can also be rented or purchased. The choice of location can be made individually.
Usually hard drives or other storage media are used as proxy servers. The offered programs can be installed on your own hard drive. The programs of the proxies typically work with standard formats. Standard formats have the advantage of being supported by all devices and allowing for fast transmission and processing.
Regarding security, a distinction can be made between transparent, anonymous and highly anonymous (elite) proxies.
Set up your own proxy server
With sufficient expertise you can also set up your own proxy server. The big disadvantage here, however, is the geographical assignment, which is still possible. For this reason the purchase of a server is preferred so that you can use all advantages. It is important to note that a server is more than just a storage space, as it has to contact the target server and request and forward the appropriate information. With the ready-to-use programs that make communication possible, setting up the proxy server is greatly simplified.
https://proxycompass.com/knowledge-base/what-is-a-proxy-server/